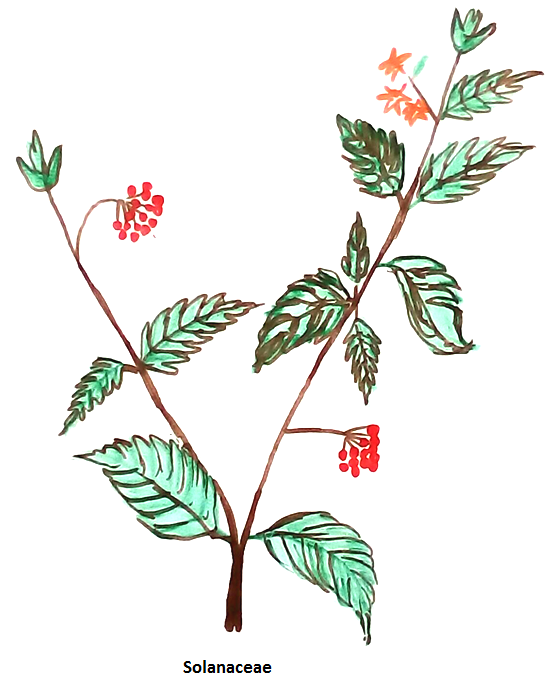
Solanacaea Family
Solanaceae is a flowering plant. Solanacaea are called night shade plant. The term solanum derived from Greek word which means night shade plant. Solanacaea plants are distributed all over the world except Antarctica. They are 98 genera and about 2700 species in the world. Major variations are found in North America and Central America. The most economical important plant of Solanacaea family is Tuberosum (potatoes).
Salient features of Solanacaea are following:
1. Plants of this family are herbs, shrubs, lianas or small trees.
2. They have internal phloem in vascular bundles around pith.
3. They contain branches hairs or often pickles.
4. This plant contains various alkaloids like nicotine, atropine, belladona etc.
5. Leaves are spirally arranged with simple, pinnately compound or trifoliate which are lacking of stipules.
6. In this family inflorescence determinate are sometimes reduced to a single flower.
7. Flowers are usually bisexual and regular in shape. They may be androecious, monoecious or dioecious.
8. Calyx contains five sepals,connate persistence which are sometimes enlarging with the fruits.
9. Corolla are of usually five petals connate rotate or tubular with lobes usually plicated (sometimes convulate) in bud, sometimes imbricate or valvate. Flowers can be solitary, grouped into cymose or axilary inflorescence.
10. Androecium contains five stamens, usually alternating with the petals and filaments epipetalous attached to a tube, anthers usually bi locular open by longitudinal slit or open with terminal pores.
11. Pollen grains usually trip or penta colpate or colporate.
12. Gynoecium are usually of two carpels oriented diagonally in flower, connate usually a disc around the gynoecium.
13. Ovary is superior and axile placentation is observed.
14. Two locules (upto five) with one anatropous to hemianatropous or amphitropous unitegmic ovule in each locules.
15. Styles are terminals, sometimes gynobasic, stigma mostly of them are three lobed.
16. Fruits are usually a berry or septicidal capsule.
17. Seeds are often flattened with straight or curved embryo.
18. This family contains oily and proteinaceous endosperm.
Different sub classes are observed in this category. They are –
Cestroideae
Geotzioideae
Nicotinoideae
Petunioideae
Schwenckioideae
Solanoideae
Economic importance of the family Solanacaea:
Used as vegetables –Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum), brinjal (S. melongena), tomatoes (S. lycopersicum), green peppers (Capsicum spp).
Used as medicinal plants –some plants of this familyalso have medicinal importance. Examples – belladonna yield atropine which is extracted from Atropa belladona. Henbane is extracted from Hyoscyamus niger. Brugmansia sanguinea.
Used as ornamental purpose- some plants are used as ornamental purpose. Examples night blooming jesmine (Cestrum nocturnum), Petunia sp, of the night or yesterday-today-tomorrow (Brunfelsia australis).
Nicotinamide – Plant species produce nicotine which is derived from tobacco.
Question and Answer on Solanacaea Family:
1. Name a tree member of Solanacaea.
Answer:
Solanum erianthum, S. America.
2. Name two climbing plant of Solanacaea.
Answer:
Solanum dulcamara, Lycium chinense.
3. Name two plants of Solanacaea with irregular flowers.
Answer:
Salpiglossis sinuata, Schizanthus pinnatus, Brunfelsia australis.
4. Which plant of Solanacaea is known as yesterday-today-tomorrow?
Answer:
Flower of this plant fade from purple to white with time. Name of the flower is Brunfelsia australis.
From Solanacaea Family to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Explain about Growth in Plants |Definition of Growth & Differentiation
Feb 27, 25 02:07 PM
Growth is a permanent increase in length or volume of an organism that brought upon by an increase in its dimensions due to synthesis of new protoplasmic material. -
Definition of Respiratory Quotient | calculation | Application | Plant
Dec 02, 24 12:09 AM
Definition of respiration quotient- the ratio of the carbon-dioxide evolved to that of the oxygen consumed by a cell, tissue, plants or animals in a given time is called respiratory quotient. It is us… -
Amphibolic Pathway | Definition | Examples | Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Jun 06, 24 10:40 AM
Definition of amphibolic pathway- Amphibolic pathway is a biochemical pathway where anabolism and catabolism are both combined together. Examples of amphibolic pathway- there are different biochemical… -
Respiratory Balance Sheet | TCA Cycle | ATP Consumption Process
Feb 18, 24 01:56 PM
The major component that produced during the photosynthesis is Glucose which is further metabolised by the different metabolic pathways like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, TCA cycle and produces energy whic… -
Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation | ETC |Diagram
Feb 04, 24 01:57 PM
It is also called ETC. Electron transfer means the process where one electron relocates from one atom to the other atom. Definition of electron transport chain - The biological process where a chains…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.