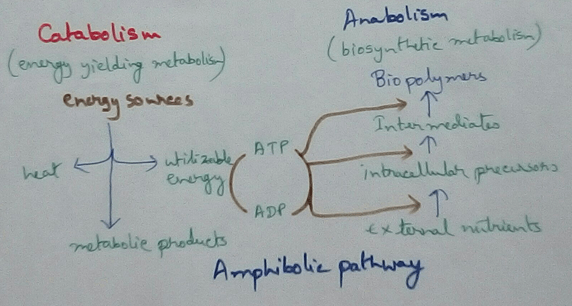
Amphibolic Pathway
Definition of Amphibolic Pathway - Amphibolic pathway is a biochemical pathway where anabolism and catabolism are both combined together.
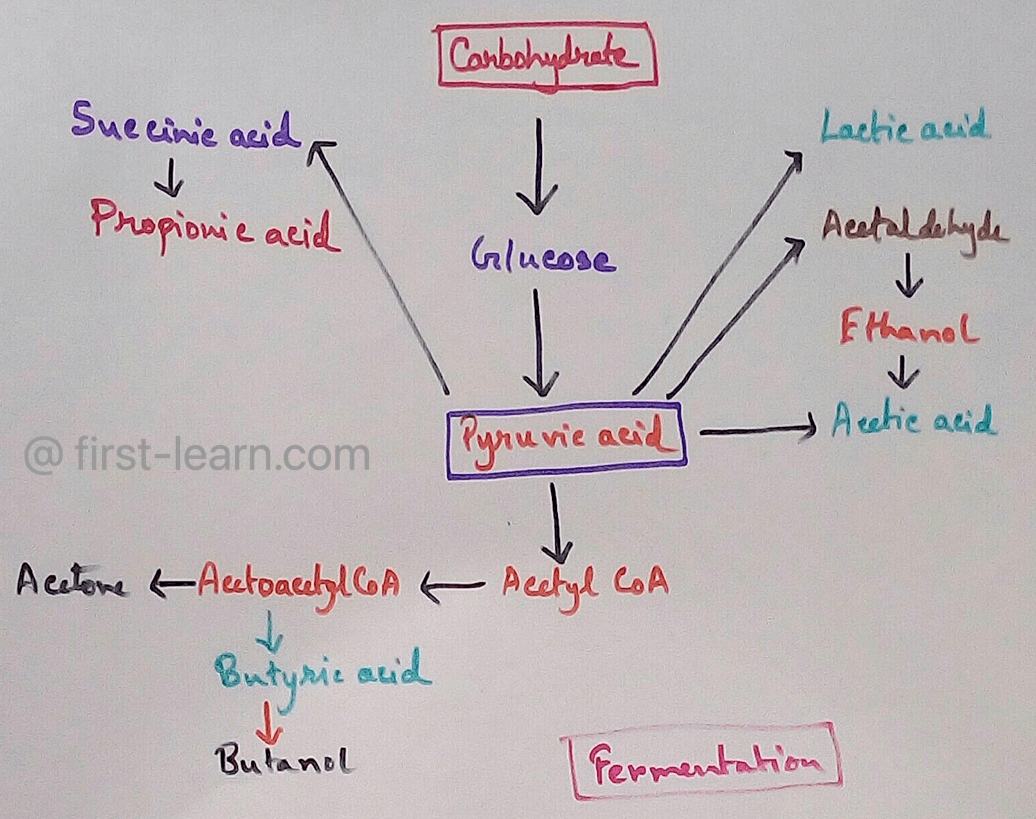
Examples of Amphibolic Pathway - there are different biochemical reactions system as amphibolic pathway. These are – Tri carboxylic acid cycle or Krebs cycle or TCA cycle is the appropriate example of this type of pathway.
Definition of Catabolism - catabolism is the broken down of complex large molecules by a series of enzyme reactions for converting complex molecules into simplier form to release energy which is used as different physiological activities in livingorganisms are called catabolism. As in this process ,there is breaking down of the substances to a simplier form is called breaking down reaction. Here the dry weight of the organisms are decreases.
Definition of Anabolism - Anabolism is a multiple step of enzymatic processby which different smallersubunits are associated together form a complex structure. As a result of this process dry weight of an organism is increased.
This process absorb energy and thus it is called endergonic process. Anabolism process is powered by catabolism has the component which are degraded to form smaller subunits, whereas small subunits are associated together to form large subunit these are the major constituent for increasing the weight and body mass in the organism.
Catabolism and anabolism are totally opposite process and their target are also totally opposite.
Production During Catabolism - This process is energy yielding process, this also gives rise to the waste products which produced during metabolism, releases energy which can be utilised by the body for different purpose,some energy is also released as heat energy for maintaining the body temperature.
The energy which is released as ATP molecules during the categories of process is used for different production of biopolymers like intracellular nutrients extracellular nutrients, different intermediate components and Carbohydrate protein, fat etc molecules. Again this biopolymers are degraded to smaller subunits or individual single-subunitforms by the catabolic process by the release of energy. Thus it can be said that catabolic process and anabolic process are wave hand to hand as both are dependent on each other.
Some Endocrinologist also decide the hormones according to their catabolic and anabolic process. Some hormones like steroid hormones are associated with synthesis of muscle mass production of protein other components like insulin of the body. Some other hormones likethyroxinsare associated with the increase of basal metabolic rate that means increases metabolism in the body.
Examples of Amphibolic Pathway -
TCA cycle as Amphibolic Pathway - Anabolic role of TCA cycle is- it is associated with the synthesis of citrate which is the precursor for the fatty acids, sterols etc. Alpha ketoglutaric acid is precursor for purines and different amines. Oxaloacetic acid is a intermediate of the TCA cycle which is precursor of different amino acids. On the other hand TCA cycle is the metabolic pathway for the organisms that leads to production of different energy molecules which then passes through the different stages of the ETS cycle to liberate energy.
Pentose Phosphate Pathway -
Entner Doudoroff Pathway - It is the major pathway for the bacteria and the lower organisms which not only provides energy ,but it produces different biomoleculesprecursors.
From Respiratory Balance Sheet Acid Cycle to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…







New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.