Definition of Respiratory Quotient
Definition of Respiration Quotient: The ratio of the carbon-dioxide evolved to that of the oxygen consumed by a cell, tissue, plants or animals in a given time is called respiratory quotient.
It is used for the basal metabolic rate in the living organisms when the BMR is calculated from the carbon dioxide production.
Respiratory Quotient Calculation: Respiratory quotient is calculated by the ratio of carbon dioxide produced by the body to the oxygen consumed by the body. Oxygen consumption can be measured by respirometer.
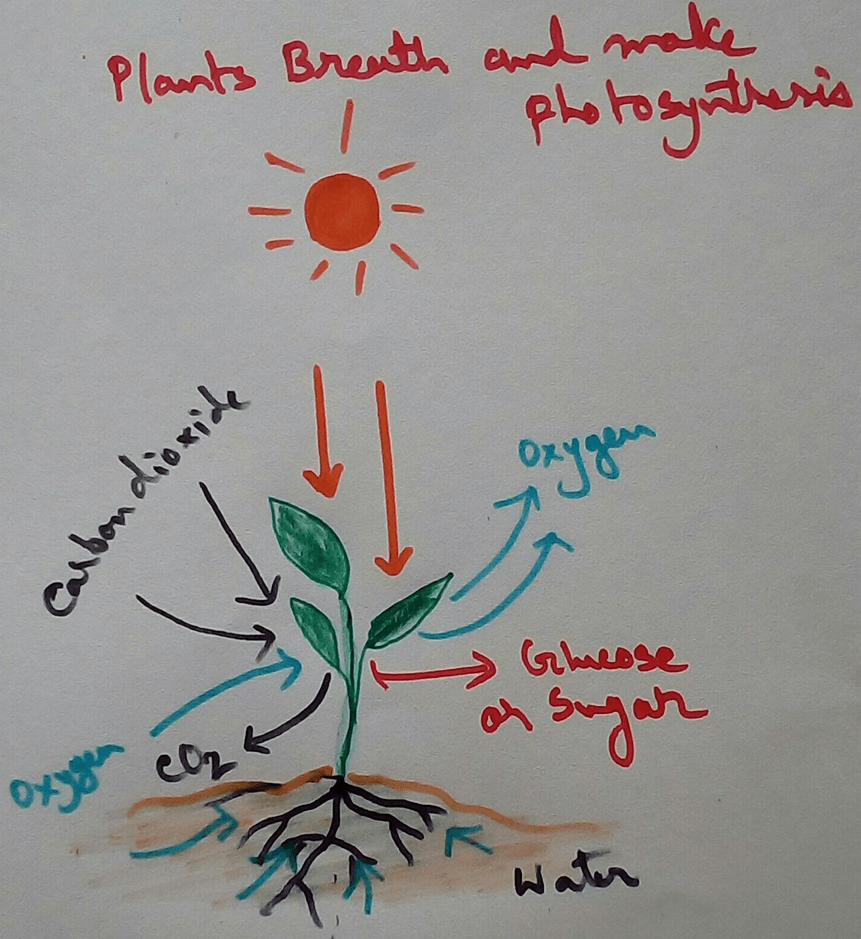
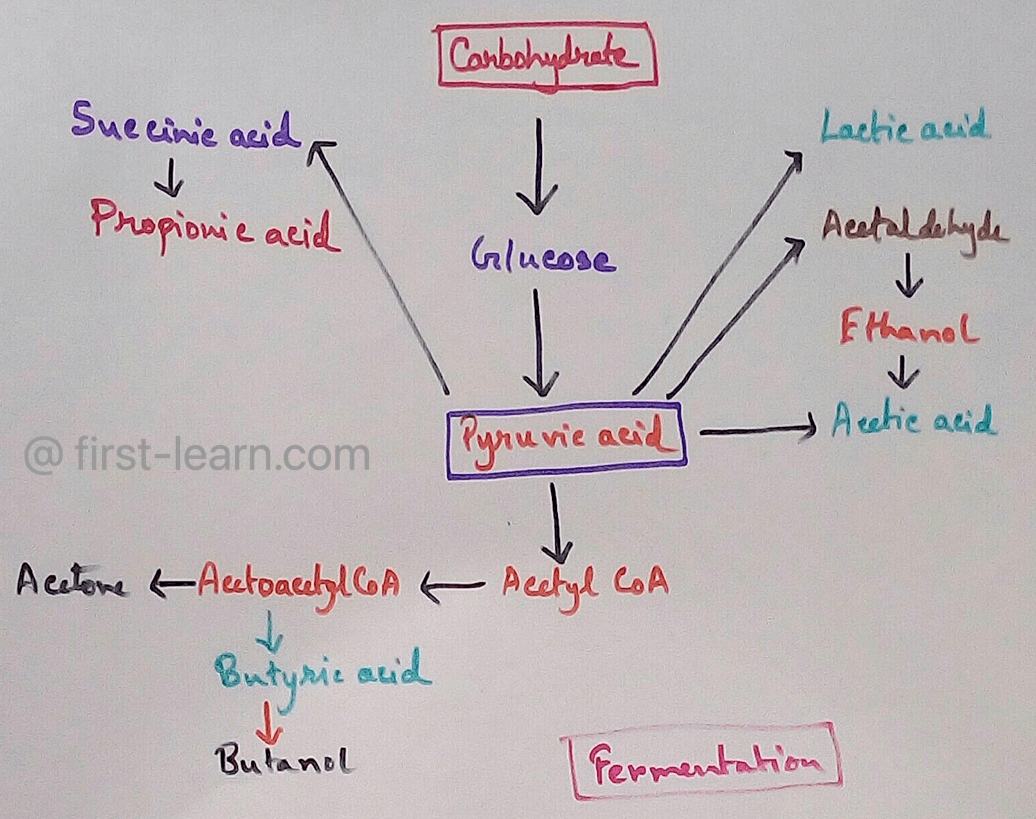
Respiratory Quotient in Plants: Respiratory quotient indicate which substrate will be metabolised as the value of Carbohydrates, Protein and fats are different from each other. The value of Carbohydrate is 1, if the substrate is Protein then the value will be .8, when the substrate is fat then the value will be .7. Value of respiratory quotient for mixed diet is .8. The value of this thing varies from one person to other according to their diet, insulin sensitivity, insulin circulation in the body and energy balance.
Application of Respiratory Quotient: Respiratory quotient has several applications for determination of several conditions-
* Chronic respiratory syndrome- Respiratory quotient is the marker to determine several chronic respiratory syndrome in organism.
* Insulin which is associated with the increase of fat storage and decreases fat oxidation is observed to be positively associated with the increase in respiratory quotient increase.
* Respiratory quotient can be used as indicators of over feeding and under feeding. As we know that under feeding will enhance the lipogenesis of stored body fat and it lowers the respiratory quotient. Overfeeding is indicated by the value of respiratory quotient is 1.
* Increase of respiratory quotient increase respiratory rate and decreases the tidal volume.
* Liver cirrhosis can be determined by the parameters of respiratory quotient in the organism.
From Definition of Respiratory Quotient to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
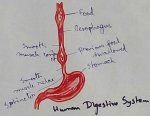
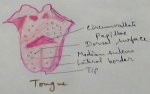
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.