Rules to Subtract Integers
Integers are positive and negative number including zero and does not include the fractional part. We will discuss about the rules for subtracting of integers. There are certain rules which will help us in better understanding of subtraction of integers. This topic will discuss how integers are subtracted when:
- One positive integer is subtracted from another positive integer.
- One negative integer is subtracted from another negative integer.
- One positive integer is subtracted from another negative integer.
- One negative integer is subtracted from another positive integer.
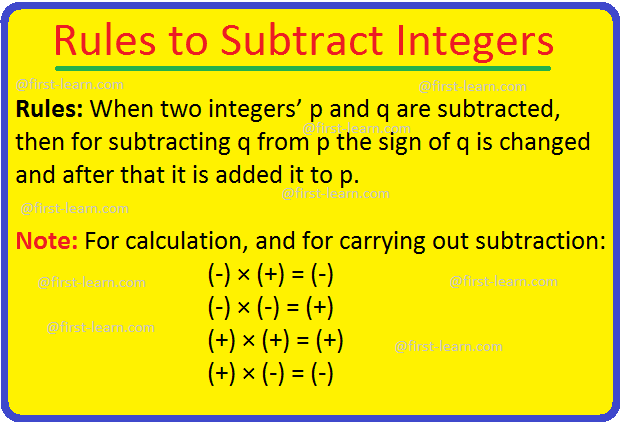
Rules: When two integers’ p and q are subtracted, then for subtracting q from p the sign of q is changed and after that it is added it to p.
Note: For calculation, and for carrying out subtraction:
- (-) × (+) = (-)
- (-) × (-) = (+)
- (+) × (+) = (+)
- (+) × (-) = (-)
When two signs are written side by side then it is considered that the two signs are multiplied.
Few examples are solved here using the rules of subtraction of integers mentioned above:
1. Subtract 10 from 5
5 – (+10)
Þ 5 – 10 = - 5
Here according to the rule negative sign and positive sign [i.e. (-) × (+) = (-)] makes negative sign. That is why – (+10) will be – 10. So it will be 5 – 10 = -5. Actually the absolute values are subtracted and in the result the value with a higher absolute value is considered.
2. Subtract -11 from 16
16 – (-11)
Þ 16 + 11 = 27
Here according to the rule negative sign and negative sign [i.e. (-) × (-) = (+)] makes positive sign. That is why – (-11) = +11. So it will be 16 + 11 = 27. Here both 16 and 11 is added to get 27.
3. Subtract 9 from -6
= - 6 – (+9)
= - 6 – 9
= -15
Here according to the rule negative sign and positive sign [i.e. (-) × (+) = (-)] makes negative sign. That is why – (+9) will be -9. So it will be - 6 – 9 = -15. Actually the absolute values are added and the result will have negative sign as both the numbers are negative.
4. Subtract -11 from -5
= -5 – (-11)
= -5 +11
= 6
Here according to the rule negative sign and negative sign [i.e. (-) × (-) = (+)] makes positive sign. Therefore – (- 11) = 11. So it will be -5 + 11 = 6. Actually the absolute values are subtracted and in the result the value with a higher absolute value is considered.
5. Subtract -5 from 16
= 16 – (- 5)
= 16 + 5
= 21
Here according to the rule negative sign and negative sign [i.e. (-) × (-) = (+)] makes positive sign. Therefore – (-5)= +5. So it will be 16 +5 = 21. Here both 16 and 5 is added to get 21.
From Rules to Subtract Integers to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Development | Definition | Leaf Development | Factors Affecting
Apr 22, 25 02:31 PM
Definition of development- development is a biological process which can be defined as the process in which there is sequence of qualitative changes towards a higher or more Complex state.It consists… -
Differentiation, Dedifferentiation and Redifferentiation | Definition
Apr 21, 25 01:16 PM
Cells from the root apical meristem and shoot apical meristem the camera that differentiate , mature to perform different functions. This process by which the cells undergo different major structural… -
Explain about Growth in Plants |Definition of Growth & Differentiation
Feb 27, 25 02:07 PM
Growth is a permanent increase in length or volume of an organism that brought upon by an increase in its dimensions due to synthesis of new protoplasmic material. -
Definition of Respiratory Quotient | calculation | Application | Plant
Dec 02, 24 12:09 AM
Definition of respiration quotient- the ratio of the carbon-dioxide evolved to that of the oxygen consumed by a cell, tissue, plants or animals in a given time is called respiratory quotient. It is us… -
Amphibolic Pathway | Definition | Examples | Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Jun 06, 24 10:40 AM
Definition of amphibolic pathway- Amphibolic pathway is a biochemical pathway where anabolism and catabolism are both combined together. Examples of amphibolic pathway- there are different biochemical…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.