Differentiation, Dedifferentiation and Redifferentiation
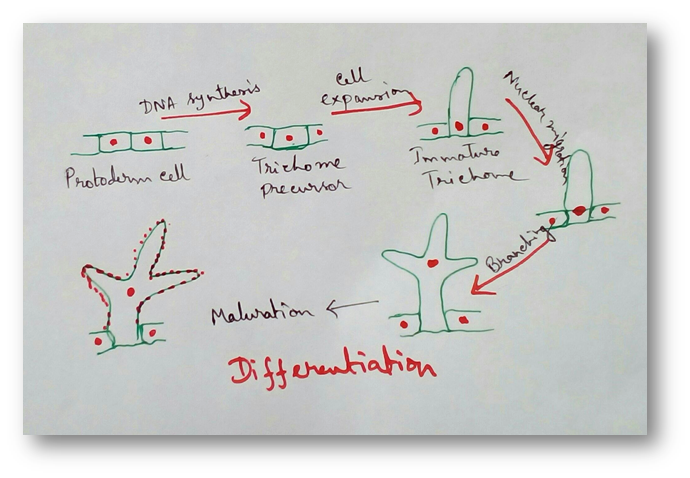
Differentiation - Cells from the root apical meristem and shoot apical meristem the camera that differentiate , mature to perform different functions. This process by which the cells undergo different major structural changes or few structural changes both in their protoplasm and in the plasma membrane are called differentiation.
The cells those are involved in this process are called differentiated cells.
It can be defined by example where a trachery element of the cells loose it’s protoplasm and developes it’s lignocellulosic secondary wall which is best suitable for the water to carry the long distance even under extreme tensed condition.
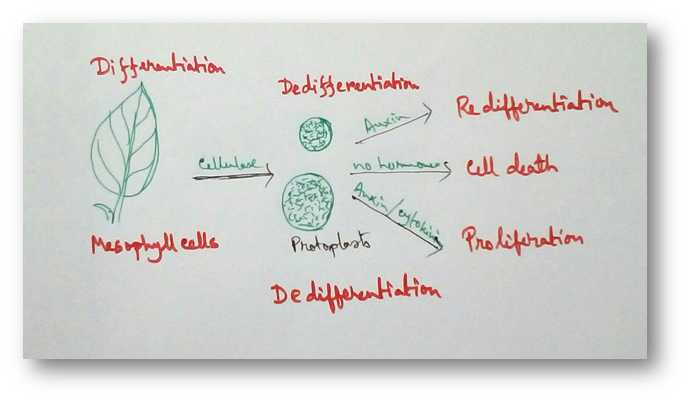
Dedifferentiation - In case of plants living differentiated cells can regain the capacity to divide mitotically under some certain condition. Sum of some events bestowed the capacity to divide once again and termed as dedifferentiation. A dedifferentiating tissue can act as meristems.
Examples are cork cambium, interfascicular vascular cambium, wound meristems.
Redifferentiation - Product of the dedifferentiating tissues that loose the ability to divide is known as redifferentiation- tissue or redifferentiated cells. This process is known as redifferentiation.
We know that growth in plants are open and even growth in plants are also open. Stem, root, phloem fibres, xylem fibres etc are developed from same origin but they have different maturation. Final structure of the cell or tissue during maturity arising from the same meristems is ditermined by the location of the cell within.
This can be explained by the example-cells that positioned distal to root apical meristem differentiated as root cap cell and this are pushed to periphery as mature epidermis.
From Differentiation, Dedifferentiation and Redifferentiation to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Differentiation, Dedifferentiation and Redifferentiation | Definition
Apr 21, 25 01:16 PM
Cells from the root apical meristem and shoot apical meristem the camera that differentiate , mature to perform different functions. This process by which the cells undergo different major structural… -
Explain about Growth in Plants |Definition of Growth & Differentiation
Feb 27, 25 02:07 PM
Growth is a permanent increase in length or volume of an organism that brought upon by an increase in its dimensions due to synthesis of new protoplasmic material. -
Definition of Respiratory Quotient | calculation | Application | Plant
Dec 02, 24 12:09 AM
Definition of respiration quotient- the ratio of the carbon-dioxide evolved to that of the oxygen consumed by a cell, tissue, plants or animals in a given time is called respiratory quotient. It is us… -
Amphibolic Pathway | Definition | Examples | Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Jun 06, 24 10:40 AM
Definition of amphibolic pathway- Amphibolic pathway is a biochemical pathway where anabolism and catabolism are both combined together. Examples of amphibolic pathway- there are different biochemical… -
Respiratory Balance Sheet | TCA Cycle | ATP Consumption Process
Feb 18, 24 01:56 PM
The major component that produced during the photosynthesis is Glucose which is further metabolised by the different metabolic pathways like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, TCA cycle and produces energy whic…



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.