Nature of the Bond Linking Monomers in Polymers
Definition of Monomer: This are molecules of low molecular weight which are combined with same type of molecules or different types of molecules to form polymer due to formation of different types of bonds. Examples of monomers are glucose, fructose, nucleotides, amino acids etc.
Definition of Polymer: polymers are the combination of different types of monomers or same types of monomers. Examples of polymers are glycogen, starch, nucleic acids etc. Glycogen is found in the muscle which is the combination of the glucose molecules and branching are observed in different locations. Starch are also polymers which are stored as carbohydrate.
Polymers are produced due to multiple repetition of the monomeric subunits and formation of polysaccharide, peptide, nucleotides etc.
Peptide Bond: Peptide bonds are formed between the amino acid molecules. As amino acid contains both carboxylic and amino group. This bond is formed between amino acids of one molecules and carboxyl group of other amino acids and water molecule is released due to formation of the bond.
Explain with Examples: Like insulin. Insulin is a hormone and is made up 9f multiple amino acid subunits which are combined with each other by the peptide bonds. Peptides bond is formed due to binding of amino group of one amino ac8d with the carboxyl group of the other amino acids and release of water molecules.
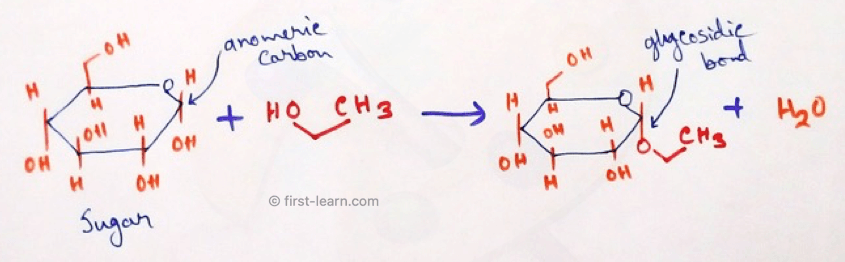
Glycosidic bond: Glycosidic bonds are type of bonds that attached one carbohydrate molecules to other molecules which may be carbohydrate molecule or may be other molecule differ from carbohydrate. Glycosidic bonds are formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group of the saccharide are attached with the hydroxyl group of the other molecule (may other than carbohydrate).
Types of Glycosidic Bonds: Generally four types of glycosidic bonds are observed. They are –
N - glycosidic bonds- sugar combined with asparagine by N glycosidic bond.
O – glycosidic bond- sugar combined with serine by the O glycosidic bond.
S glycosidic bond-
C glycosidic bond-
Explain with Examples: When glucose residues which are monomers are combined together and bonded by glycosidic bond they form glycogen or starch molecules which are polysaccharides. Branching are observed in different region of the polymers.
Nucleotide Bond: Nucleotides are called the subunits of the nucleic acids. Different nucleotides are associated together to form the nucleic acids. Nucleotides are made up of ribose or deoxyribose sugar, nitrogen bases, phosphate. Ribose sugar are found in RNA and deoxyribose sugar are found in DNA. In DNA adenine are combined with thymine, whereas guanine is combined with cytosine. But in RNA uracil is found in place of thymine.
Explain with Examples: The nucleotide sequences carry the code of the respective amino acids. This is then transcribe to the messenger RNA or mRNA . Then this RNA undergoes translation as t RNA carries the anti code and combined with the codon which is combined with mRNA and form the respective amino acids. These amino acids are combined together to form polypeptide chains and protein.
From Nature of the Bond Linking Monomers in Polymers to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…













New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.