Metabolic Basis for Living
Definition of metabolism: Metabolism is the process by which chemical energy is required to maintain the life of living organisms.
Importance of Metabolism- Metabolism have three major functions. Such as-
1. Metabolism is associated with breakdown of food or fuel to release energy.
2. It also provides nutrients and energy to the all living beings for their physiological activities.
3. Metabolism is also associated with the production of building blocks of the protein, amino acids, nucleic acids.
4. It also provides energy for the removal of waste materials from the body.
5. Metabolism is a continuous process in living organisms because every reaction remain in continuous phase due to equilibrium conditions.
Types of Metabolism: Generally the metabolism can be divided into two categories-
Catabolism: Catabolism means degradation of the complex compound into simpler form and release energy required for the physiological activities, growth, development etc. Here dry weight is decreased. In this mechanism complex compound is broken down to form simple components. These are occur in different types . They are –
Breaking down of polysaccharides: Breaking down of polysaccharides first start with the initiation of the rebranding of the components (carbohydrate). Glycolysis is an example of the catabolic process where glucose 6 phosphate is broken down into the pyruvic acid molecules. It is then again pass through the Tricarboxylic acid cycle for further break down.
Breaking down of proteins: Proteins are broken down into amino acid by different proteolytic enzymes. Examples are protease or Pepsin which hydrolyses the peptide bonds of the protein and converts this stable structure of protein into simple amino acids.
Breaking down of lipid molecules: lipases are involved in the breakdown of lipid molecules in fatty acids and glycerol.
Anabolism: Anabolism is the just opposite process of catabolism. Here different simple components are combined together to form different major primary subunits. Those are – glucose molecules, amino acids molecules, nucleotide molecules etc. This molecules are combined with other element to produce carbohydrate molecules, proteins DNA ,RNA molecules. This process causes increase of dry weight and produces building blocks of the body. In anabolism different simple molecules are combined to form complex molecules. These occurs by different pathways. These are –
Formation of proteins from amino acids: Amino acids are the basic subunits of protein. They are combined with each other by peptide bond. This bond is for between the amino and carboxyl group of the amino acids. There are also hydrogen bond, disulphide bridge, chemical bonds involve in the protein structure that gives protein secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure.
Formation of phospholipid from glycerol and fat: Different lipid molecules combined with phosphate to form phospholipid. This is major component of cell membrane.
Formation of polysaccharides from monosaccharides: Different monosaccharides are associated to form disaccharide, then these molecules are combined by the formation of 1-4 glycosidic linkage or 1-6 glycosidic linkage together. Associatedly they give rise to the polysaccharides.
Formation of DNA and RNA: Nucleotides are associated with Pentose sugar and formed DNA and RNA molecules.
FromMetabolic Basis for Living to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…
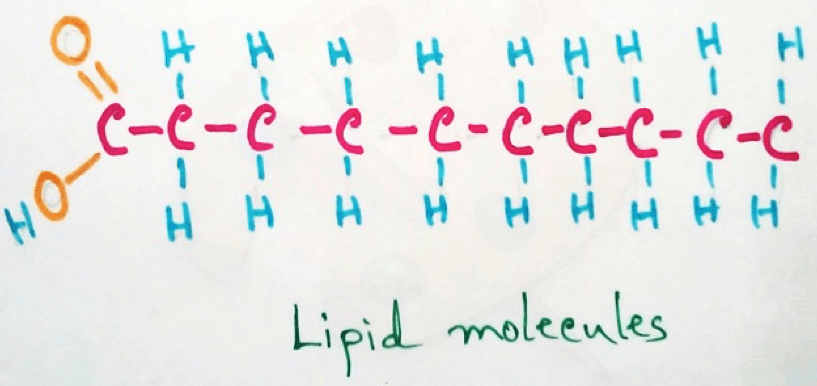










New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.