Biomacromolecules
Definition of Biomacromolecules - Biomacromolecules are molecules that has molecular weight of more than 1000 Dalton and are found in the acid soluble pool of the chemical analysis of living tissue.
These are large sized complex molecules which are of high molecular weight which are commonly formed through condensation or polymerisation of repeated units of micromolecules.
Different Types of Macromolecules - Major types of macromolecules are polysaccharides, proteins, amino acids etc.
Polysaccharide:
Definition of Polysaccharide - Polysaccharides are large sized carbohydrates that are formed by condensation of a number of monosaccharides. Polysaccharides are formed due to the glycosidic linkage between the monosaccharides.
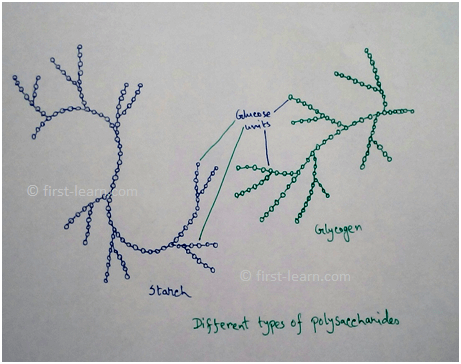
Types of polysaccharide - structurally polysaccharide can be of two types. These are –homopolysaccharides and heteropolysaccharide. Homopolysaccharides are type of polysaccharide which is made up of one type of monosaccharides (examples are glucan, galactan, fructan etc.). On the other hand heteropolysaccharides are polysaccharide which is made up of different types of monosaccharides (examples are chitin, pectin, hemicellulose etc).
Functionally polysaccharide are of three types-
1. Storage Polysaccharide – These type of polysaccharide reserved foodthat can hydrolysed to produce monosaccharide sugars. Examples are glycogen, starch, inulin etc.
2. Structural Polysaccharide - These are fibrous polysaccharide that formed exoskeleton of arthropods. Examples are cellulose, hemicellulose etc.
3. Mucopolysacharides - Slime or mucilage producing heteropolysaccharides. Examples are pectins, hyaluronic acid, chondroitin etc.
Proteins:
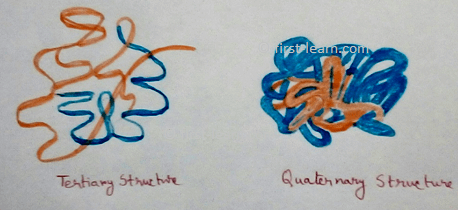
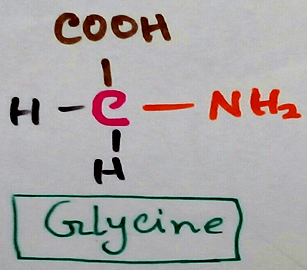
Definition of Proteins - In 1838 Berzelius described amino acid polymers which are consist of polymers of amino acids (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur). According to number of protein molecules or polypeptides they can be divided into monomeric protein (examples are haemoglobin, insulin,immunoglobulin etc.). When amino acids are bonded by peptidoglycan bond and is called primary structure. When there are different bonds are formed (hydrogen, disulphide, salt bridge etc are developed)theprimary structure of protein are folded in different positions as bonds are formed between the amino acids and different secondary structure is formed called alpha helix, beta pleated sheet. Further folding occurs due to tertiary structure formation and quaternary structure formation of the protein.
This formation occurs due to the stable structure of the protein with minimum energy state. Functions of proteins are associated with contraction, hormones, enzymes, transport, receptors, phosphoprotein, blood clotting, immunity etc.
Types of Proteins - According to the structure of protein molecules it can be divided into two- simple protein and conjugated protein. Examples of simple protein are albumin, globulins etc. But if the protein molecules are combined with other elements such as metal they are called conjugated protein. Examples of conjugated proteins are haemoglobin where haem is the metal part (iron), and the globin part is called proteins.
Nucleic Acids - This is a complex nucleur structure that form due to the combination of nucleotides. These nucleotides are combined to form DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid). They are called carrier of the hereditary characteristics.
DNA - Deoxyribonucleic acid is helically coiled macromolecules that is made up of two antiparallel polydeoxyribonucleotide chains which held together by hydrogen bonds. This two chains are coiled around a common axis.
From Biomacromolecules to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like… -
Explain Transport of Gases | External Respiration | Tissue Respiration
Oct 09, 25 11:35 PM
In humans gaseous exchange is completed in the following ways the steps are - External Respiration or Breathing - Breathing in false taking in of Oxygen and giving out of carbon dioxide in the body. M…
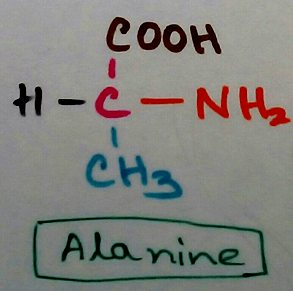















New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.