Classification and Nomenclature of Enzymes
Introduction - In earlier days enzymes were called by some ambiguous and uninformative name such as – ptyalin, zymase, trypsin, errosion etc. Later their name are done by the addition of suffix 'ase' after the name of the substrate on which they act.
Types of Enzymes - There are different types of enzyme according to their reaction and catalytic power International Union of Biochemistry divided into six major groups. This groups are follows -
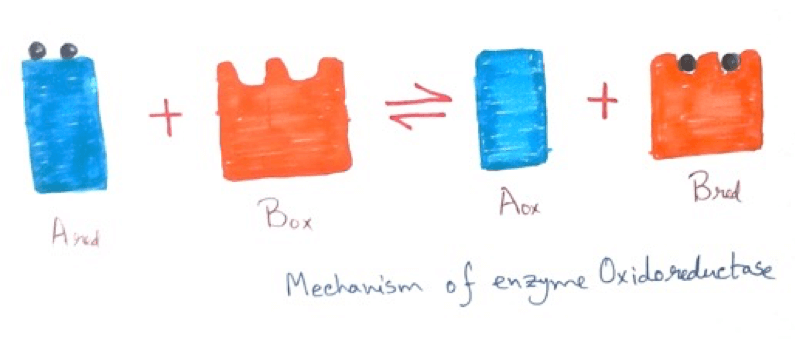
1. Oxidoreductase - This type of enzymes are associated with the oxidation reduction reaction. This enzymes are of two types . They are – (i) Oxidase (ii) Dehydrogenase.
(i) Oxidase - This type of enzymes causes addition of oxygen to the substrate. Examples of this enzymes are amino acid oxidase, cytochrome oxidase etc.
(ii) Dehydrogenase - This type of enzyme remove hydrogen from the substrate. Examples of this type of enzymes are succinic dehydrogenase, malic dehydrogenase etc.
Other type of enzymes are reductase which is associated with the reduction of the substrate by addition of hydrogen atoms to the substrate. Examples of the reductase are retinene reductase.
2. Transferase - Transferase are group of enzymes that transfer specific functional group from one substrate to the other substrate. Examples of this group of enzymes are amino transferase, hexokinase, Cholin acetylase etc.
3. Hydrolases - This group of enzymes are associated with the hydrolytic reaction of compound. Examples of this group are amylase, peptidase,lipase etc. These enzymes causes breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones by addition of water molecules and split off specific co valent bond. This process is called hydrolysis.
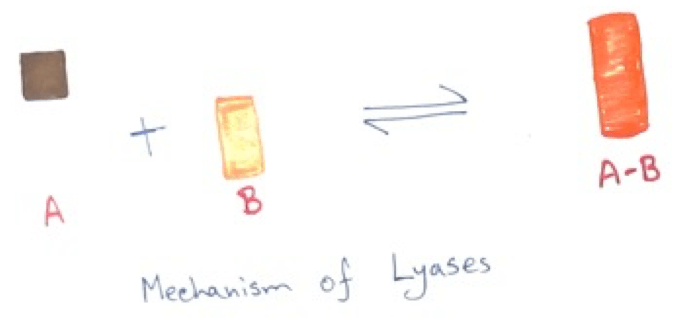
4. Lyases - This group of enzyme causes removal of groups from the substrate or addition of group to the substrate. This is occurred by the process called hydrolysis, oxidation, reduction etc. Examples of this enzymes are – Carboxylase, fumarase, agrinosuccinase, decarboxylase etc.
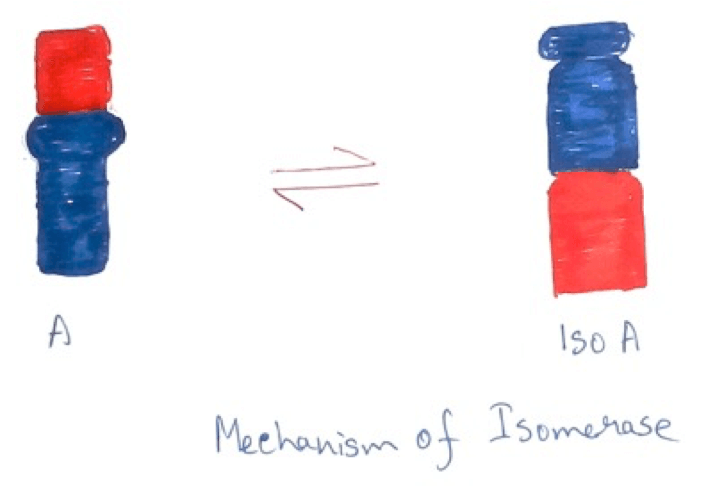
5. Isomerase - Enzymes of this group are associated with the conversion of isomers. Examples are Phosphohexose isomerase, triose phosphate isomerase.
6. Ligase or Synthetase or Synthase - In this group of enzyme ,it catalyses linking of two compounds by energy requiring reactions. Examples of this type of enzymes are glycogen Synthase, fatty acid synthase etc.
Nomenclature of the Enzyme - According to the international system of enzyme classification- Name of an enzyme is considered both the substrate on which it acts and the type of reaction it catalyses.
Here first will be the name of the substrate and the second part will be the type of reaction it catalyses.
The ending of the enzyme name will be with ‘ ase’ .
Nomenclature explain with example- lactic dehydrogenase is an enzyme . Whose first part is formed from lactic acid as it acts as substrate and this enzyme is associated with dehydrogenation means oxidation . Thus the second part of the enzyme name dehydrogenase (as -ase will be added to the end).
Questions and Answers on Classification and Nomenclature of Enzymes:
1.What is the function of lipase?
Lipase splits lipid.
2. What does protease do?
It splits the protein.
3. What is the role of amylase?
This enzyme splits the amylum or starch.
From Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…












New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.