Living Things Grow
All living things grow.
Let us see our photograph when we were born. We can see a very small baby in
that picture. Perhaps we cannot recognize that it is our own photo.
When we were born, we were very small. Since then we have been growing continuously. We can look at our photograph when we were about 4 years old. We can look ourselves today. We surely look different. We have grown up. After some years, we will grow into an adult. So, it shows that a child grows into an adult.
Similarly like us, plants and animals also grow.
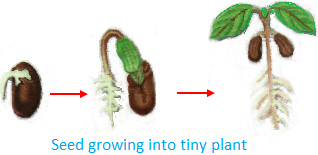
Seed grow into a tiny plant. A tiny plant grows into a big plant or a tree.
A chick grows into a cock or hen. A kitten grows into a cat.
So, all living things grow.
Now, think about non-living things. Think about the doll with which we played is of the same size even today. The doll has not grown so, non-living things does not grow.
Practice the activity to check this on your own.
Let us take two small plastic bags and fill each bag with soil. Plant some seeds in one bag and a pen in another bag. Water both the bags for several days.
What do we see after several days?
The seeds have grown into tiny plants whereas; the pen has not grown at all.
So from here we come to know that non-living things do not grow.
Can we name any non-living thing which grows? Do our book, pencil and bag grows?
No. No one grows at all. So, all living things grow while non-living things do not grow.
Living Things Need Food and Water
Animals and PlantsFrom Living Things Grow to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Explain about Growth in Plants |Definition of Growth & Differentiation
Feb 27, 25 02:07 PM
Growth is a permanent increase in length or volume of an organism that brought upon by an increase in its dimensions due to synthesis of new protoplasmic material. -
Definition of Respiratory Quotient | calculation | Application | Plant
Dec 02, 24 12:09 AM
Definition of respiration quotient- the ratio of the carbon-dioxide evolved to that of the oxygen consumed by a cell, tissue, plants or animals in a given time is called respiratory quotient. It is us… -
Amphibolic Pathway | Definition | Examples | Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Jun 06, 24 10:40 AM
Definition of amphibolic pathway- Amphibolic pathway is a biochemical pathway where anabolism and catabolism are both combined together. Examples of amphibolic pathway- there are different biochemical… -
Respiratory Balance Sheet | TCA Cycle | ATP Consumption Process
Feb 18, 24 01:56 PM
The major component that produced during the photosynthesis is Glucose which is further metabolised by the different metabolic pathways like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, TCA cycle and produces energy whic… -
Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation | ETC |Diagram
Feb 04, 24 01:57 PM
It is also called ETC. Electron transfer means the process where one electron relocates from one atom to the other atom. Definition of electron transport chain - The biological process where a chains…




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.