How many Pigments are Involved in Photosynthesis?
How many pigments are involved in the process called photosynthesis?
Definition of Pigments - Pigments are the molecules that absorbs light of specific wavelengths release the other means absorbs energy and provide that for transformation of electrons into next level.
Types of Pigments - There are different types of pigments in the plants. Among them some are main pigments and other are accessory pigments. Main pigments are chlorophyll A , chlorophyll B etc. On the other hand accessory pigments are carotenoid, xanthophylls, phycocyanin etc.
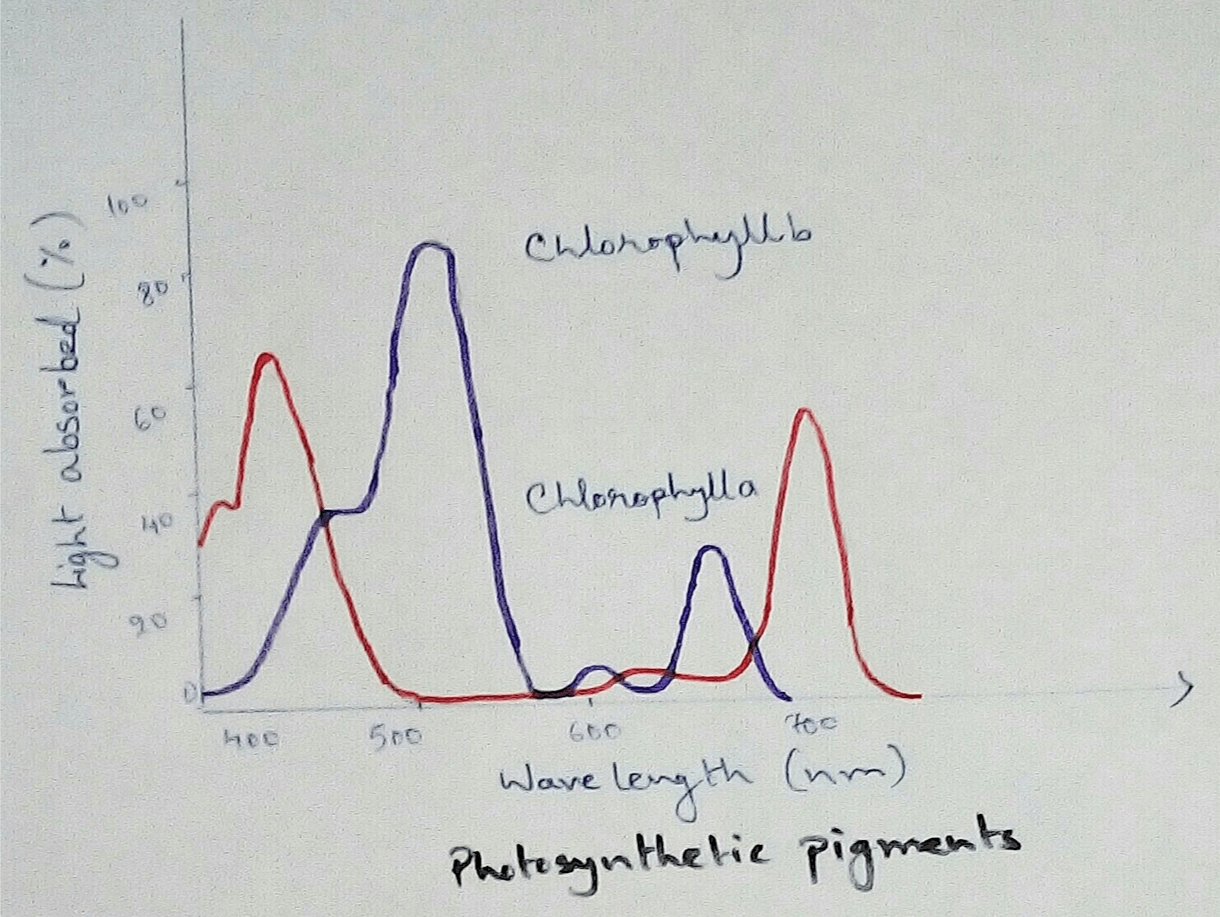
Chlorophyll A - Chlorophyll A is the that absorbs light at 430 nm which is blue light and also absorb red light at 660 nm. It contains a magnesium ion (Mg++) at the center of the pigments which remain attached by the pyrol chains. It contains hydrophobic phytol chain which remain embedded in the lipid layer as it is fat soluble components. Rest of the chains are known as tetra pyrolic chain which surrounded outside the membrane. This pigments are the most abundant pigments that found in the most of the green plants. It looks like green in colour as it cannot absorb green light it only reflects the green light. The metal magnesium present in the pyrol of the pigments show different valency in different time as it is very flexible for different state of reaction. Whenever electrons required it can donate or some times during its requirement it can accept. It acts as both electron acceptor and electron donater. This is the only pigment that can trap the solar energy from the sun.
Chlorophyll B - Chlorophyll B is the second abundant pigments that is found in the green plants which has many similarities with the chlorophyll A pigments structure. It absorbs light rays from 452 nm to 642 nm. It is not so abundant like chlorophyll A. Probably it is seem to be evaluated later after chlorophyll A. Main function of chlorophyll B is to help the plants to absorb light in a broader range.
Carotenoid - Carotenoid are the accessory pigments that we get in abundant of the plants. It seems to be yellow, red, orange to us. As it absorbs light of the wave length 450 nm to 560 nm. Structure of the carotenoid is hydrophobic in nature and thus it is fat soluble. Carotenoids are the pigments that protect the plants from UV radiation. It acts as antioxidant and the free radicals that produce in different parts of the plant body is neutralize by this pigments. It reacts with the compound present in the plant's body due to continuous exposure of the sunlight and the harmful rays that fallen from the sun.
Xanthophylls - This are the fourth type of pigments essential for photosynthesis. Actually xanthophylls are the oxidised carotenoids which and are usually contains oxygen. They are generally yellow and red in colour and donot absorbed light like carotenoid. They are fat soluble in nature, thus embedded in the membrane.
Anthocyanins - This pigments are fifth class of photosynthetic pigments. They are not fat soluble, they are soluble in water.
From How many Pigments are Involved in Photosynthesis? to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…















New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.