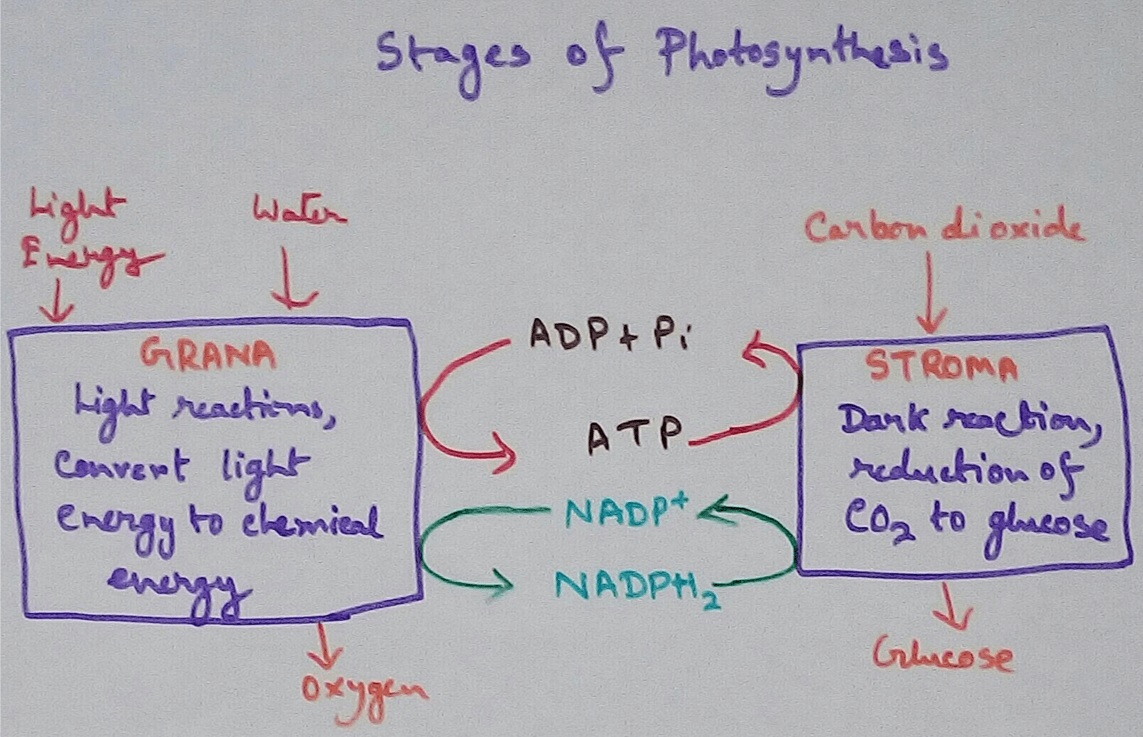
Where are the ATP and NADPH used in Photosynthesis
ATP and ADP are energy molecules Which produced during light reaction and that is utilised in the dark reaction bye release of energy.
Production of ATP and ADP during Light Reaction:
Uses of ATP and NADPH - ATP and NADPH (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) are have role same of Calvin cycle is almost same like krebs cycle as the products that produced during the light reaction enters the Calvin cycle as a carbon dioxide and release as glucose.
Here ATP are used as high energy molecules and in NADPH acts as reducing agents which provides electron to form glucose. Calvin cycle produces three carbon containing compounds glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
Reaction:
6 CO2 + 12 (NADPH + H+) + 18 ATP → C6H12O6 + 12 NADP+ + 18 ADP + 18 Pi + 6 molecules of water.
Calvin cycle is made up of three phase among them the middle one is the reduction. In this phase two step reaction take place by the hydrolysis of ATP and reduction of 3 phosphoglycerate to phosphoglyceraldehyde.
Reaction:
Phosphorylate 3 phosphoglycerate enzyme transfer phosphate from ATP molecules and causes the following reaction-
* Uses 6 molecules of ATP to produce six molecules of 1,3 bis phosphoglyceric acid.
12 PGA + 12 ATP- → 12 molecules of 1,3 di PGA + 12 ADP.
* It acts as primer of 1 ,3 phosphoglyceric acid and add electrons from NADPH.
* Electrons of NADPH reduce carboxyl group of 1,3 bis phosphoglycerate to 3 phosphoglyceralde.
12 molecules of 1,3 Di PGA + 12 NADPH2 - → 12 PGAlD + 12 NADP.
The third step of Calvin cycle is regeneration of the initial compounds that is ribulose bis phosphate-
This energy required three molecules of ATP and produces RuBP molecules that is produced and is available for start of the cycle again.
5 PGAlD (Phosphoglyceraldehyde Glyceraldehyde) → 5 molecules of DHAP.
For the net synthesis of three molecules of glucose 3phosphate, 9 molecules of ATP are required and 6 molecules of NADPH2 are required.
Raw material for Calvin cycle is glucose 3 phosphate that is used for synthesis of glucose and other carbohydrates. Here 18 molecules of ATP is required and 12 molecules of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) is required for production of one Glucose molecule.
Blackmans law of limiting factor- factors that affect the reaction is known as Black nails law of limiting factors. These are light intensity carbon dioxide concentration etc.
From ATP and NADPH used in Photosynthesis to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…















New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.