Translocation of Solutes
Definition of Translocation - Translocation is a process by which transport of food materials from the source or point of manufacture two different growing regions of the plant take place.
As we all know that water is transported by the roots and the food produced in the leaves are must be transported to different parts of the plant for providing nutrient and energy the two types of transport system are required.
Xylem tissue is associated with the conduction of water. It is a complex tissue where there are four types of tissues are involved. Among them three of them are dead – tracheid, trachea, xylem fibre. Another one is a the xylem parenchyma which is the only living among the xylem tissues.
Phloem tissue is associated with the conduction of the food that produced in the leaves.
As we all know that Green Leaves make food by absorption of water through the roots uptake of carbon dioxide from the air by the stomata and in presence of Sunlight. This reaction causes conversion of chemical energy solar energy to chemical energy. Green plants are the only living organisms that can trap sunlight from the environment. Then the green plants were taken as food by the herbivores then herbivores are taken as food by the other consumers. As a result of this, the energy that is trapped inside the food pass through plant to herbivores, herbivores to consumers. But the percentage of energy transfer reduces from herbivores to other level of consumer.
Food is manufactured in the leaves and due to photosynthesis glucose is produced, this glucose is immediately converted into insoluble starch in the leaf and storage for the future use.During the night plants are not able to make photosynthesis due to absence of Sunlight the use the starchto be converted into soluble sugar and transported to various parts of the plants to provide nutrients to different area.
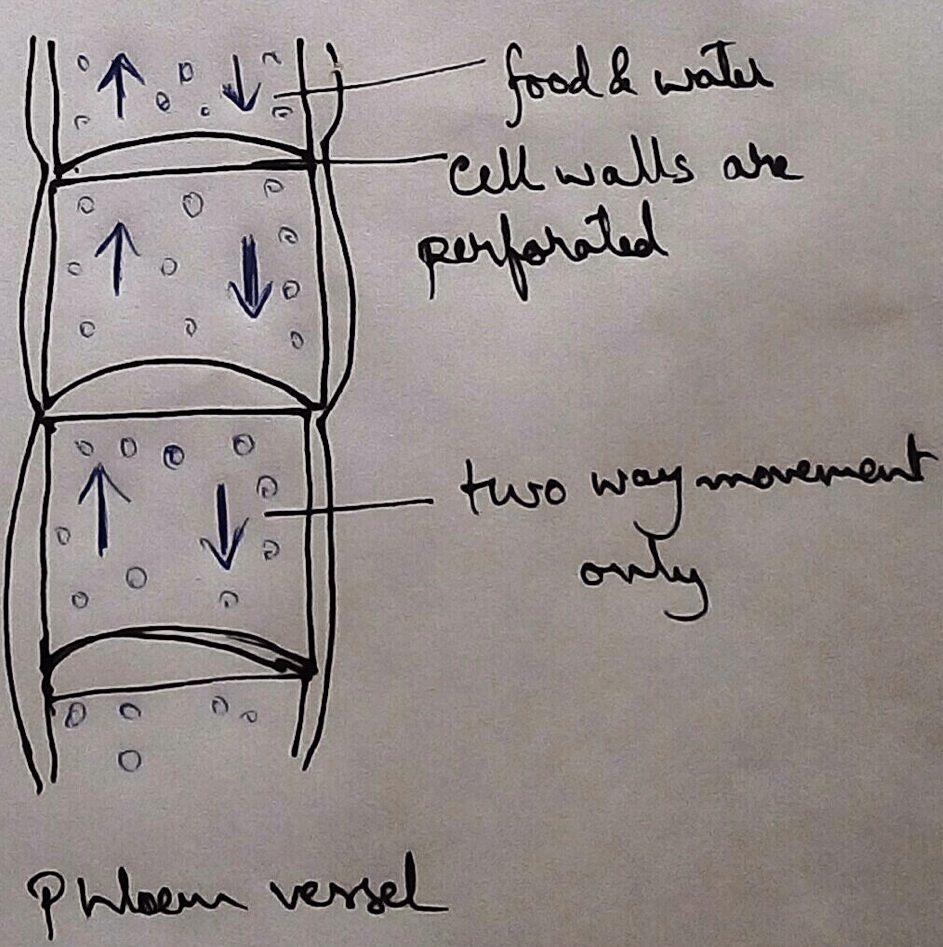
Structure of Phloem - Phloem is the sets of cells and tissue system that associated with the transport of food through the leaves and branches. Phloem is made up of four types of tissues- thus it is called complex tissues. It has three living and one non-living tissue. Three living components are phloem parenchyma cells, sieve plate, companion cells. The only non living cells are phloem fibres. Phloem tissues are having sieve cells and sieve plate. This tubes are arranged one by one to form a pipe like structure, and between the pipes the walls are dissolved to form a continuous capillary by which the food produced in the leaves are transported.
Direction of the Translocation - Solutes through the phloem is transported in both upward and downward direction. As its main function is to transport the minerals to different parts of the plant tissues.
Question and Answers on Translocation of Solutes:
What is the name of the special type of tissue that found in the vascular bundles between xylem and phloem?
Xylem and Phloem are all together called vascular tissue or vascular bundles. Cambium is present between this two types of tissues.
From Translocation of Solutes to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…












New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.