The Sky
We see the sun, the moon and the stars in the sky. We see the sun during the day. In the day, we will see sun and clouds in the sky. The sun is a huge ball of fire. It is hot and bright. It is very far away from us. The sun is a star. It is the nearest star to the earth. It rises in the east every morning and new day beings. It sets in the west every evening. When the sun sets, it becomes dark. Then night begins. At night we will see moon and stars in the sky. The motion of earth around the sun causes formation of day and night. The sun gives us heat and light. The sun is stationary. It is a ball of burning gases.
The Moon and the stars
We see the moon and the stars in the sky at night. The moon is smaller than the sun. It is cool. The moon has no light of its own. It reflects the light of the sun. The moon keeps on changing its shape every night. When the moon looks like a ball, it is called full moon. Full moon is seen once in a month. There are millions of stars in the sky. They have their own light. The stars are different sizes. Some stars are even bigger than the sun. They look small because they are very far away from us.
The Earth
We live on the earth. The earth is a planet. It is smaller than the sun. It is bigger than the moon. The earth moves round the sun in a definite path. It also moves on its axis.
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
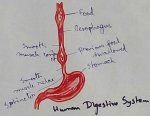
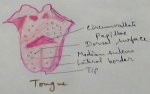
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.