Simple Tissues and Complex Tissues
Simple Tissues – Simple permanent tissue made up of those permanent cells that is similar in structure, origin and function. It is of three types –
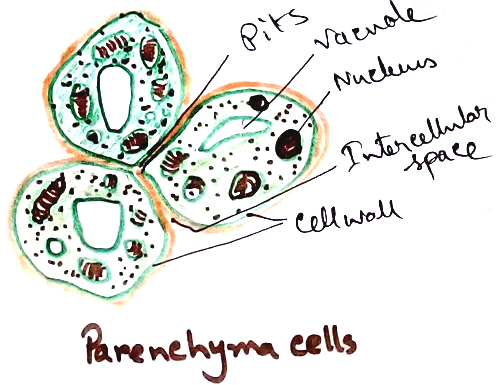
Parenchyma - It is simple tissue that is made up of isodiametric living cell which has thin cellulose walls. This tissue is responsible for storage of food, slow conduction and turgidity of soft tissues. It is found inside the stem ,root as cortex and pith, pulp of fruit, endosperm of seed, parts of vascular tissues, leaf interior etc. Epidermis is made up of modified parenchymatous cell.
Different types of parenchyma are – Chlorenchyma (having chloroplasts and takes part in photosynthesis), Aerenchyma (network of parenchyma cells are enclosed in large network cavities,e.g. aquatic plants), Epidermis (cutinised parenchyma that forms covering layer), guard cell (a pair of specially thickened small reniform or dumbbell cells that create a pore between them due to differential swelling), Prosenchyma (elongated fibre like parenchyma), Storage parenchyma (cells are large vacuolate store mucilages as food which are required for storing water in the cells of succulent), idioblast (specialised parenchyma cells that contain crystal, tannin, oils), Secretory cells, phloem parenchyma, epiblema.
Collenchyma – This tissue is found in hypodermis of dicot stem,petioles, climbing stem. It is made of isodiametric or elongated living cells having unevenly thick pecto- cellulosic walls. It provides both mechanical strength and elasticity of plant and is called living mechanical tissue. Depending upon thickenings it is of – Lamellate, lacunate, angular.
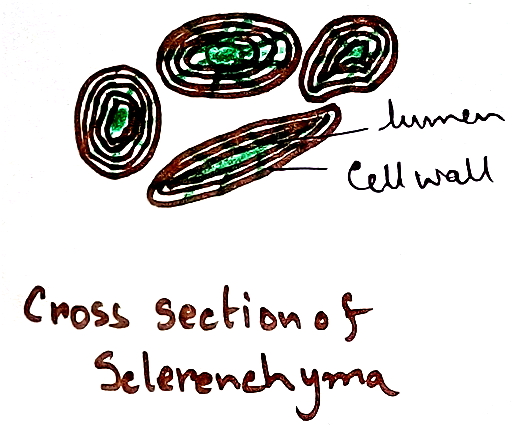
Sclerenchyma - This type of permanent tissue are made up of dead cells. Highly thickened wall (lignin), narrow lumen. It is of two types –
Sclerenchyma fibres – Elongated ,spindle shaped cells ,with pointed or oblique end walls. Commercial fibres are derived from this . According to origin it is of three types – surface fibres (cotton, coconut), bast fibres (jute, hemp), leaf fibres (sisal, Manila).
Sclereids - Broad sclerenchyma cells that develop from parenchyma - which provide stiffness.
Complex Tissues –this are type of permanent tissue that is developed from more than one type of cell that co ordinate their activities to perform a similar function. This type of tissue is observed in vascular plants and is responsible for conduction of water and food. Vascular bundles are made up of xylem and phloem.
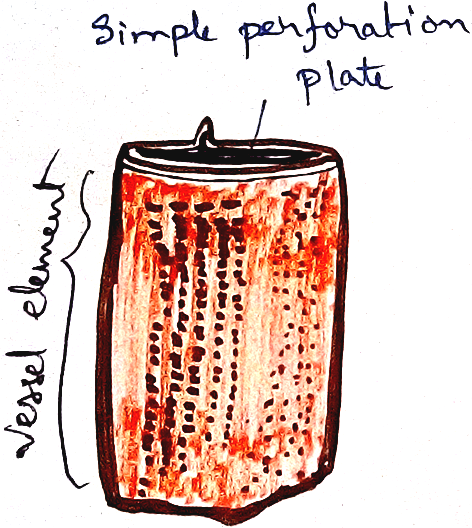
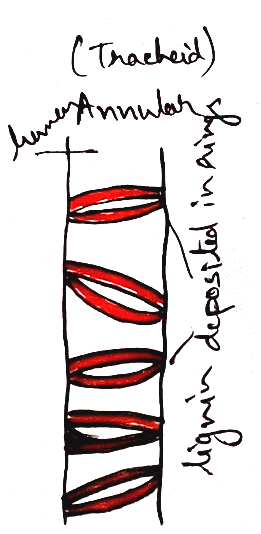
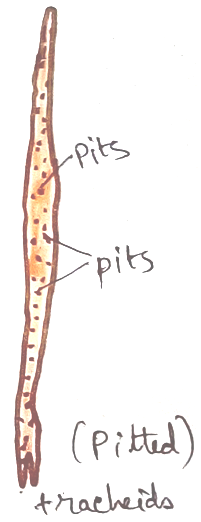
Xylem – xylem is responsible before conducting water and dissolved minerals from root to the upward direction of the plant towards leaf. It is made up of four types of tissues. Three of them are dead tissue and one is living. Dead tissues are – tracheids, trachea, xylem fibre. On the other hand it contains only one living tissue that is xylem parenchyma.
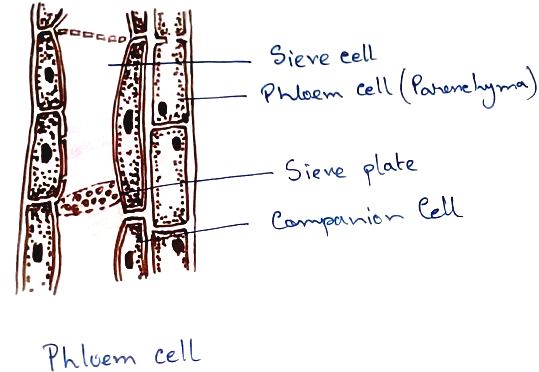
Phloem - Phloem tissue is another conducting tissue of plant that supply food (which is produced in leaves ) from the leaves to different parts of the plant downwards and lateral side of the plant. It consists of four types of tissue. Among them three are living and one is nonliving. Three types of living tissue are sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma. The dead one is phloem fibres (flax, jute, hemp).
Vascular bundles are two types - radial and conjoint.
From Simple Tissues and Complex Tissues to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.