Regions of Root and Modifications of Root
Modifications of tap roots:
1. Fleshy tap roots - Tap roots become swallowed as it stores food. Some of the plants with fleshy tap roots may initially possess reduced stem and radical leaves.
• Conical – Fleshy root is like a cone. It is observed in carrots.
• Fusiform – The root is swollen like a spindle, being thickets in the middle and narrowing towards both apex and base. In Indian Radish the base is formed of swallowed hypocotyl.
• Napiform – It is like a top or sphere that thins out abruptly at the apex. Swallowed part is formed jointly by hypocotyl and tap root of Beet.
• Tuberous – Tap root is thickened except at the base without producing a definite shape.
Example: Mirabilis, Trichosanthes.
2. Nodulated Roots – In legumes root contains irregular structure called nodules or tubercles. Symbiotic bacteria take shelter in the nodules and they supply nitrogen to the plant. Different pulses (pea plant, gram etc) show this thing.
3. Pneumatophores - In mangrove plants this type of root is observed. They are short, vertical, negatively geotrophic which plays role in plants respiration.
Example: Heritiera, Avicennia etc.
4. Buttress Roots – This roots are laterally compressed horizontal roots which travel along the ground for some distance and provide extra mechanical support.
Example: Rubber tree, Simbal, peepal etc.
5. Reproductive roots – Some of the tap roots and their branches develop adventitious buds and help in vegetative reproduction.
Example: Populus, Dalbergia etc.
Modifications of Adventitious Roots System:
1. Fibrous Root – This are very thin thread like structure which often developed in a group, provide firm anchorage to the plant.
Example: Grass, wheat etc.
2. Fleshy Adventitious Roots – Adventitious roots are swallowed due to storage of food. They are of different types-
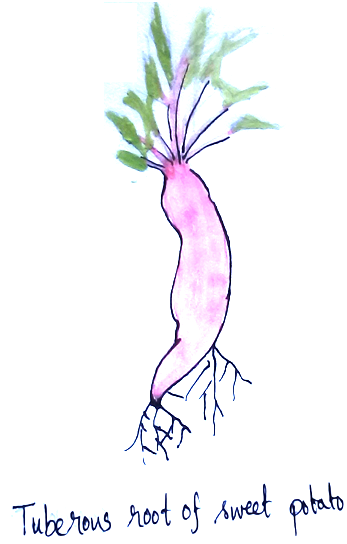
• Root tubers – Sweet potato
• Fasciculated roots - Asparagus, Dahlia.
• Palmate root - Orchis.
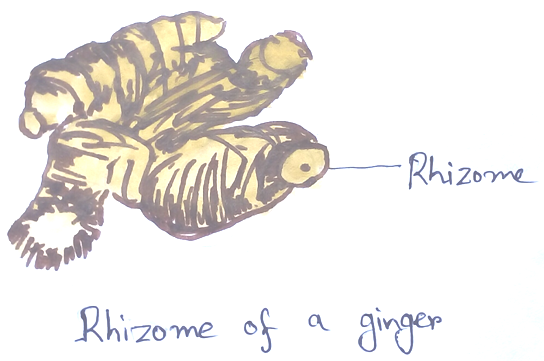
• Nodule roots – Maranta, mango ginger.
• Moniliform root - Mormordica, some grasses.
• Annulated root - Cephaelis.
3. Prop Roots - They are pillar like give support to the plant.
Example: Banyan tree.
4. Stilt Roots – They are stout oblique roots which arise in circular whorls from the lower nodes of the stem.
Example: Maize, sugarcane.
5. Hausteria or Parasitic Roots – roots penetrate the host to suck nutrition.
Example: Cuscuta, Viscum.
6. Climbing Roots - Root help the plant to climb by penetrating the cracks of the support.
Example: Ivy, Vanilla.
7. Photosynthetic or Assimilatory Root – Roots able to make photosynthesis.
Example: Trapa, Taeniophyllum.
8. Epiphytic Hygroscopic Root hang in the air possesses velamen for absorbing moisture.
Example: Orchids, Vanda etc.
9. Epiphyllous Root – Roots develop from leaves specifically from injured part.
Example: Bryophyllum, Begonia.
10. Floating Root – Air is stored in roots (spongy) help the plant to float.
Example: Jussiaea.
11. Root Thorn - Roots are modified into thorn and spine.
Example: Acanthorhiza
12. Contractile Roots– Roots can shrink and bring an underground organ to its proper depth.
Example: Crocus, Freesia.
13. Leaf Roots - One leaf of each node modified to balance in water.
Example: Salvinia.
14. Reproductive Roots – Develop adventitious buds.
Example: Sweet potato, Dahlia.
From Classify an Unknown Specimen to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like… -
Explain Transport of Gases | External Respiration | Tissue Respiration
Oct 09, 25 11:35 PM
In humans gaseous exchange is completed in the following ways the steps are - External Respiration or Breathing - Breathing in false taking in of Oxygen and giving out of carbon dioxide in the body. M…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.