Multiplication of Decimal Numbers
This topic would deal with multiplication of decimal numbers. Previously in case of addition and subtraction we have seen that we need to change the set of decimal numbers to be added or subtracted into like decimal fractions but here changing into like decimal fraction is not required. Here we need to multiply two decimal numbers as we multiply whole numbers without considering the decimal point. After finding out the product count the number of decimal places in both the numbers (i.e. the multiplicand and the multiplier) and in the result also counts as many places from the last place towards the right to place the decimal point.
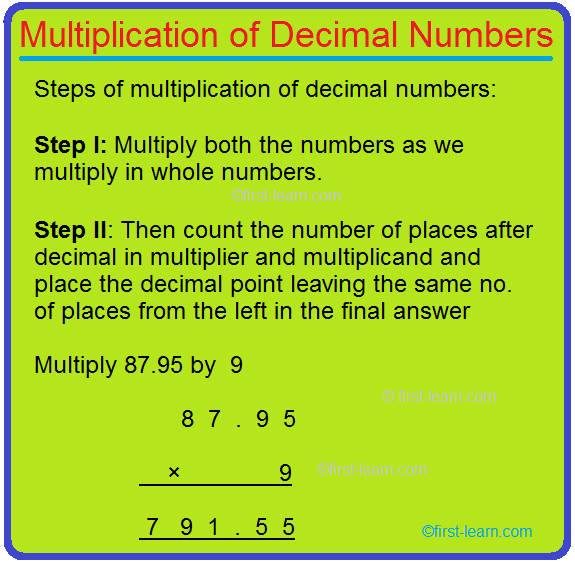
Steps of multiplication of decimal numbers:
Step I: Multiply both the numbers as we multiply in whole numbers.
Step II: Then count the number of places after decimal in multiplier and multiplicand and place the decimal point leaving the same no. of places from the left in the final answer
Here are few examples on multiplication of decimal numbers:
1. Multiply 87.95 by 9
Solution:
8 7 . 9 5
× 9
7 9 1 . 5 5
Here as we multiply in case of whole numbers we will multiply first 9 with 5 to get 45 but we will only write 5 and 4 will be carried over. Then in tenths place 9 is multiplied with 9 to get 81 and 4 carrying from hundredths place to make it 85 in the tenths place and we will write 5 and 8 would be carried over to the units place. Now 9 multiplied by 7 is 63 and carry 8 would make it 71 and hence would write 1 and 7 carrying. Now 9 multiplied by 8 is 72 and 7 carry would make it 79. As in the multiplicand the no. of decimal place is 2 all together. The decimal will be placed leaving 2 places from the left of the number.
2. Multiply 40.62 by 2.3
Solution:
4 0 . 6 2
× 2 . 3
1 2 1 8 6
8 1 2 4 0
9 3 . 4 2 6
Here as we multiply in case of whole numbers we will multiply first 3 with 2 to get 6 and then 3 with 6 to get 18 where 8 is written and 1 carried over. Again 3 is multiplied by 0 to get 0 and 8 carry over hence will write 8. Again 3 is multiplied with 4 to get 12. In the second row 2 is multiplied with 2 to get 4 and then 2 is multiplied with 6 to get 12 but we will only write 2 with 1 carrying. For the units place 2 is multiplied with 0 to get 0 and 1 is carried over and hence will write 1 and finally 2 is multiplied with 4 to get 8. The decimal will be placed leaving 3 places from the left of the number. As in the multiplier and multiplicand the no. of decimal place is 3 all together.
From Multiplication of Decimal Numbers to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like… -
Explain Transport of Gases | External Respiration | Tissue Respiration
Oct 09, 25 11:35 PM
In humans gaseous exchange is completed in the following ways the steps are - External Respiration or Breathing - Breathing in false taking in of Oxygen and giving out of carbon dioxide in the body. M…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.