Multiplication of a Decimal by 10, 100, 1000
This topic would deal with multiplication of decimal with 10, 100 and 1000. We have learnt multiplication of decimal numbers with other decimal numbers or whole numbers. Here we will deal with multiplication of decimal number with 10, 100, and 1000. In order to multiply a decimal number with 10, 100 or 1000 the decimal point moves right depending on the number of zeros.
For the purpose of multiplication with 10, 100 or 1000 the decimal point moves to the right. The number of places the decimal point will move depends on the number of zeros. Suppose a decimal number is multiplied with 10 then the decimal point will move one place right. If the decimal number is multiplied with 100 then the decimal point will move 2 places to the right if it is multiplied with 1000 then it will move 3 places right and so on.
For example:
5.568 × 100
The decimal point will move 2 places to the right as there are 2 zeros. Therefore the decimal will be placed after the digit 6. That means
= 556.8
Here are few more examples to illustrate multiplication of decimal by 10, 100 and 1000
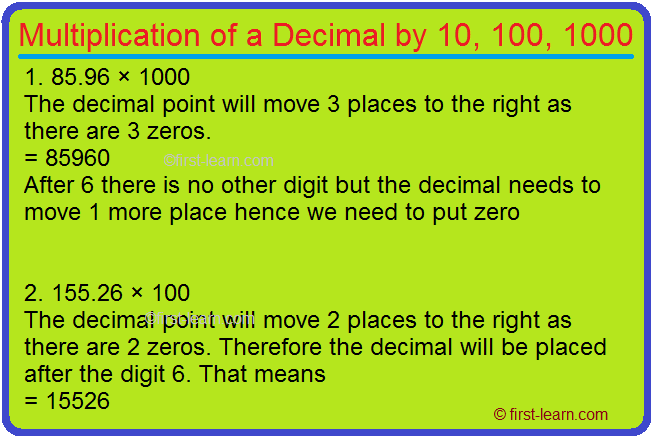
1. 85.96 × 1000
The decimal point will move 3 places to the right as there are 3 zeros.
= 85960
After 6 there is no other digit but the decimal needs to move 1 more place hence we need to put zero
2. 155.26 × 100
The decimal point will move 2 places to the right as there are 2 zeros. Therefore the decimal will be placed after the digit 6. That means
= 15526
3. 50.96 × 10
The decimal point will move 1 places to the right as there are 1 zeros. Therefore the decimal will be placed after the digit 9. That means
= 509.6
4. 7.854 × 10
The decimal point will move 1 places to the right as there are 1 zeros. Therefore the decimal will be placed after the digit 8. That means
= 78.54
5. 0.554752 × 10000
The decimal point will move 4 places to the right as there are 4 zeros. Therefore the decimal will be placed after the digit 7. That means
= 5547.52
6. 703.96 × 1000
The decimal point will move 3 places to the right as there are 3 zeros.
= 703960
After 6 there is no other digit but the decimal needs to move 1 more place hence we need to put zero
7. 2.374 × 100
The decimal point will move 2 places to the right as there are 2 zeros. Therefore the decimal will be placed after the digit 7. That means
= 237.4
8. 425.58 × 1000
The decimal point will move 3 places to the right as there are 3 zeros.
= 425580
After 8 there is no other digit but the decimal needs to move 1 more place hence we need to put zero
From Multiplication of a Decimal by 10, 100, 1000 to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like… -
Explain Transport of Gases | External Respiration | Tissue Respiration
Oct 09, 25 11:35 PM
In humans gaseous exchange is completed in the following ways the steps are - External Respiration or Breathing - Breathing in false taking in of Oxygen and giving out of carbon dioxide in the body. M… -
Kind and Number of Teeth | Location of Teeth in Mouth | Care of Teeth
Sep 11, 25 12:52 AM
Kind and Number of Teeth






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.