Movement and Shelter of Animals
There are different movement and shelter of animals. We know animals move from place to place in search of food, water and shelter. Animals move using certain body parts. Different animals have different types of movements. Animals like lions, tigers, deer, cats and dogs can walk and run.
Cows, goats and deer have hooved feet. This helps them to walk and run even on rocky land.
Tigers, dogs, bears, cats and wolves have padded feet. This helps them to move silently while hunting. Their sharp claws can hold the prey and tear its flesh.
Animals like frogs, rabbits and hares jump or hop about. They have strong legs. The front legs are short while the hind legs are long. The hind legs push the body to jump forward. They land on the strong front legs.
Note:
The fastest animal on land is the cheetah. The cheetah is known to run at a speed of over 100 km per hour over a short distance, while chasing other animals.
Animals like earthworms, snails and snakes crawl.
Insects like bees have a pair of wings. This helps them to fly.
Fish glide and swim in water. The body of a fish is shaped like a boat. It has fins, a tail and a smooth body. These enable it to swim easily in water.
Turtles use their tails and legs as flippers to swim in water.
Crocodiles use their tails and feet as paddles to swim in water.
Lizards can walk upside down on ceilings. They do so with the help of their hollow feet which have pads on the underside of the toes.
In movement and shelter of animals we already know the different movements of different animals now we will discuss about the shelters of different animals. Every animal has a shelter of its own. It uses this shelter to raise its young ones or to keep itself safe from its enemies.
Wild animals like deer, lions, elephants, wolves live in groups. They live in tall grass or under thick bushes.
Snakes, worms and many insects live in holes in the soil. Rabbits make burrows in the soil.
Fishes live in water, while birds live in nests.
Domestic animals such as dogs, cats, horses, hens and pigs live in dwelling places made by man.
As these animals help us in many ways, we must take care of them.
We must provide them with clean shelters and sufficient food and water. We must give them medical treatment when they are ill.
Animals are living things. They are nature’s gift to us. We should not tease or trouble them. We must not kill them. We must always love and protect them.
Animals and its Feeding Habits
Movement and Shelter of Animals
Nesting HabitsFrom Movement and Shelter of Animals to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
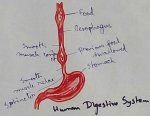
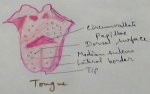
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.