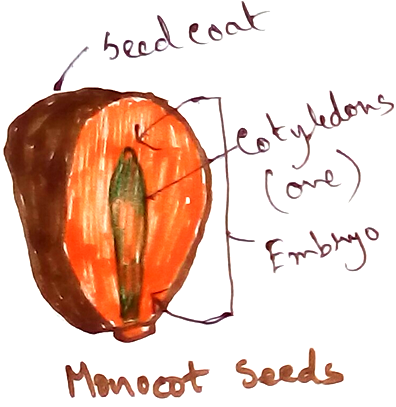
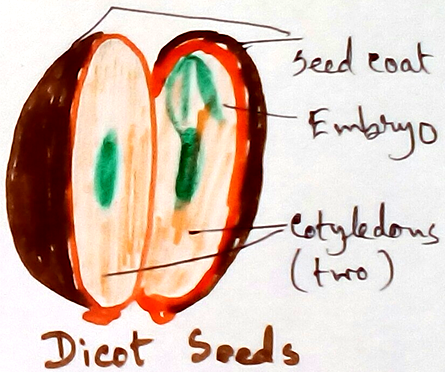
Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous Plants
Primary dicot stem - Characteristics features of primary dicot stems are-
* Epidermis is present at the outer most part of the stem which is made up of rectangular barrel shaped cells.
* It has distinct cuticle, multicellular cutinised hair called trichomes and stomata at places.
* Stomata contains kidney shaped guard cell.
* From inner layer to the epidermis is called hypodermis which is made up of collenchymatous cell.
* Hypodermis is followed by parenchymatous cortex.
* Endodermis are known as starch sheath.
* Endodermis is without cadparian strips.
* Pericycle is situated just behind the endodermis.
* Sclerenchymatous pericycle occurs as bundle caps.
* Vascular bundles lie in a ring which is called eustele.
* They are wedge shaped, conjoint, collateral and open.
* Xylem is end arch means centrifugal which having radial rows of angular vessels where tracheids fibre and parenchyma cell is present in between and around them.
* A strip of fascicular cambium occurs between the xylem and phloem that helps in secondary growth.
* Secondary growth pushes the primary xylem and primary phloem away from each other.
* In between the vascular bundles medullary rays are present and they lie radially elongated parenchyma cells.
* The pith lies in the center.
Monocot Stem -
Characteristics features of monocot stem are -
* The stem is covered by epidermis. It is rectangular barrel shaped and silica is deposited on the outer surface of the stem causes stiffness and provide protection to the stem.
* A layer of cuticle is present.
* In some places stomata is present and they have dumb bell shaped guard cells.
* Hypodermis contain 2-3 layered , sclerenchymatous and ground tissue is undifferentiated.
* Endodermis , pericycle,pith are not recognisable.
* Ground tissue consists of parenchyma cells which store food.
* Vascular bundles are numerous and possesses atactostele.
* Vascular bundles are oval in shape and surrounded by sclerenchymatous cell which is called fibrovascular bundles.
* Type of each vascular bundles is collateral,conjoint and closed.
* As phloem lies outside the xylem is called endarch.
* Protoxylem has a schizo lysigenous cavity which is called protoxylem cavity.
* Metaxylem has two lateral rounded vessels where protoxylem has 1-3 small oval vessels.
* Tracheids are observed between.
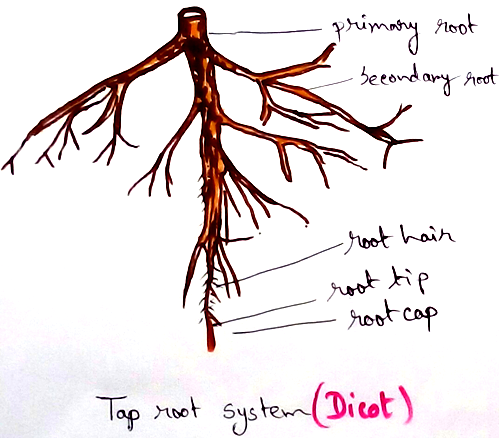
Primary Dicot Root – Characteristics features of dicot roots are –
* Outside the root is covered by an layer called epiblema or piliferous layer (uncutinised thin layer rivalled rectangular cells).
* Some of the cells of this piliferous layer form thin layer tubular out growths called root hairs.
* These are specialized for water absorption from soil interspaces.
* Other epiblema cells can also absorbed water and minerals from the soils.
* In the other part of the monocot plant the root hair shrivel and epiblema converted to thick walled.
* Epiblema have several layers of thick cortex.
* Cortex is followed by endodermis (a layer which is compactly arranged by barrel shaped cells that possess ligno- Siberian thickenings which are called cadparian strips.
* Endodermis function as check post as where one or more layer of pericycle lies below endodermis.
* Pericycle gives rise to lateral roots which is the part of the vascular cambium and whole of cork cambium.
* Vascular bundles consists ofalternate, radial bundles (2-8) of xylem and phloem.
* Xylem is exarch or centripetal means protoxylem is situated outside.
* Pith may be present or absent. If the pith is absent or small metaxylem of different bundles meet at the center.
* Depending upon the number of xylem present root can be diarch ,triarch, tetrarch etc.
* Xylem is made up of polygonal vessels, where the protoxylem vessels being narrow and small in size.
* Phloem consists of sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and occasional phloem fibres.
* Conjunctive parenchyma occurs between xylem and phloem bundles and it secondarily form main part of the vascular cambium.
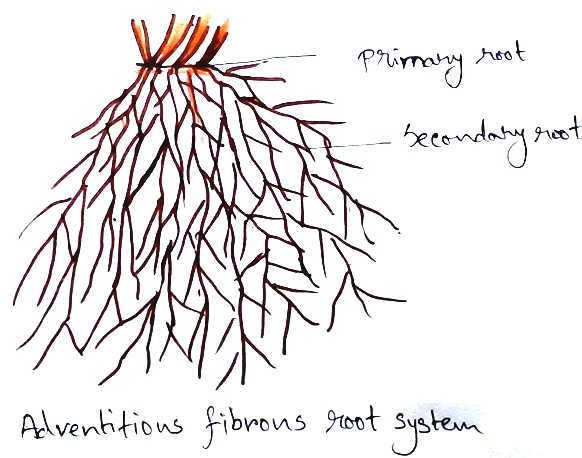
Monocot Root: Characteristics features of monocot roots are -
* Outer layer of the root is called epiblema or piliferous layer.
* The cells of this layer are oval rectangular ,thin walled and uncutinised.
* Some of the cells that give rise to tubular root hairs for the absorption of water from the soil interspaces.
* The area of the root which is comparatively older, the root hairs shrivel and epiblema cells either become thick walled or are shed.
* Cortex are several layers thick and is made up of parenchymatous cell.They make participation in storing food and conduct sap from outside.
* The outer layer and older part of the cortex thickened to form protective layers called exodermis.
* Endodermis is a single compact layer made up of barrel shaped cells. The young cell that possess ligno- suberised casparian thickenings. Whereas in older parts the endodermal cells become thick walled except it is opposite in protoxylem points. These cells are called passage cells.
* Pericycle is made up of one or more layer of parenchymatous cell.
* Pericycle gives rise to root branches where the older part of the cell wall become thickened.
* Pith cells store food and vascular strands occurs around a central pith.
* Vascular strand contains a large number of alternate radial bundles of xylem and phloem.
* Xylem is exarch and centripetal.
* Vascular strand is polyarch that is embedded in conjunctive tissue.
* Xylem contains oval rounded vessels.
* Phloem is made up of sieve tubes and companion cells and secondary growth is absent.
* Very rare species are there those are having vascular bundles less than 8.
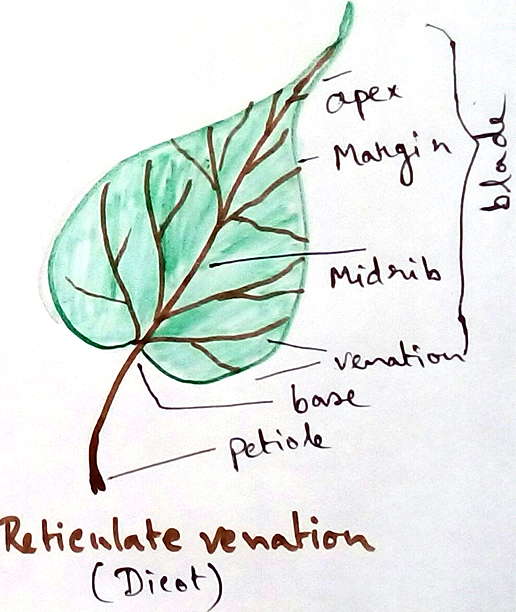
Leaves of dicot plants - Characteristics features of leaves of dicot plants are –
* Upper layer of the leaf contains thick and lower layer contains thin cuticles.
* Intercellular space is bigger in leaf.
* leaves of dicot plants donot contain bulliformed cells.
* Number of stomata in both side of the leaves of plant in not equal ,it is more in lower surface of the leaves.
* Reticulate venation is observed in the leaves of dicot plant.
* Contains large and small vascular bundles.
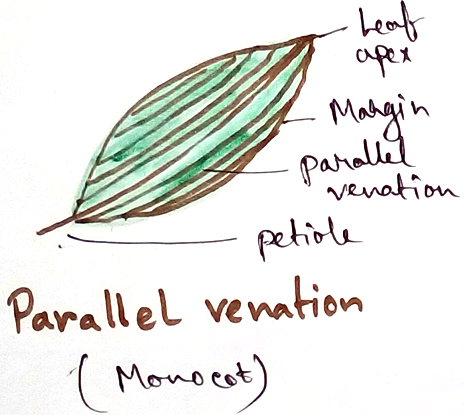
Leaves of monocot plant- Characteristics features of leaves of monocot plants are
* Both layer of the leaf contains thin cuticles.
* The intercellular space between the cells are less.
* Leaves of monocot plants contains equal number of stomata in both side of the leaves.
* They have bulliformed cells in their leaves.
* Parallel venation is observed in monocot plant leaves.
* Monocot leaves have large vascular bundles.
From Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous Plants to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.