Major Groups of Protozoa
Protozoa can be divided into different phylum. They are following-
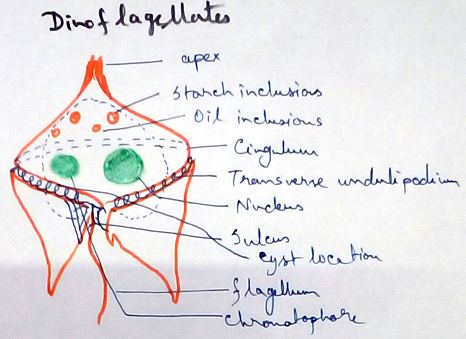
I. Zooflagellata: it includes the protozoans which have flagella for locomotion. The cell is covered by periplast. Holistic or absorptive nutritions are observed.
According to number of flagella zooflagellates can be divided into-
- Single flagellate (Trypanosoma)
- Four to six flagella in Trichomonas
- Eight flagellants in Giardia
II. Sarcodina: Here locomotory organs are pseudopodia. According to shape of pseudopodia, it can be divided into-
- Lobopodia – broad pseudopodia observed.
- Filopodia - narrow pseudopodia are observed.
- Axopodia - narrow with support pseudopodia is observed.
- Reticulopodia - reticulate pseudopodia is observed.
Sarcodina can be solitary or colonial, with or without a shell, uninucleate, binucleate or multinucleated. Holistic nutrition is observed.Excretion is amonotelic. It consists of ameboids, heliozoans, foraminifera’s and radiolarian.
A. Amoebids - body shape is changeable. Food capturing and locomotion are performed by lobopodia.e. g. Amoeba, Entamoeba, etc.
B. Heliozoans - The protists posses radiating axopodia-.e. g actinophrys.
C. Foraminiferans – The bottom dwelling sarcodines have one or more chambered calcareous shell with extra capsular protoplasm giving rise to reticulopodia. White chalk of cretaceous, Egyptians pyramid, limes of eosin are foraminiferans by origin. E.g. Elphidium, Globigerina etc.
D. Radiolarians – Free floating sarcodines are large sized and multinucleated. Chromosome number is high, as Aulocantha possesses the maximum number of chromosome, 1600. Radiolarians have siliceous perforated capsule. Intracellular capsular part has nucleic and vacuoles. Extracellular part consists of pseudopodia (filopodia-axopodia or reticulopodia). E.g. Acanthoamoeba, Callozoum.
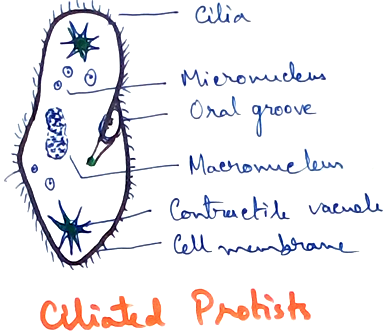
III. Cilliata: The protists have numerous cilia, a pellicle, regions of ingestion and version and nuclear dimorphism (reproductive micronucleus and vegetative macronucleus). A few forms are sedentary or colonial. Ciliates are fastest protists with a maximum speed of 2mm/sec. It is 1mm/sec in paramecium.It contains trichocyst and cillia. Vorticella is stalked ciliates found attached to various objects inside fresh water ponds. Stalk is contractile. The body is like an inverted bell thickened on the rim to form collar or lip.
Paramecium is free living fresh water ciliate which is popularly known as slipper organism.
V. Parasitic protozoans: they are also called sporozoans. They are spore forming protozoans. It lacks locomotory structures and contractile vacuoles. The body is covered by pellicle or cuticles.Plasmodium vivaxis malarial parasite spread by female anopheles mosquito. Life cycle of Plasmodium is cinematic and triphasic (schizogony, gamogony and sporogony).
Uncommon protozoan’s parasites
- Acanthoamoeba- Cyst forming parasite in pharynx and brain, causing necrosis, keratitis, abscesses and meningo- encephalitis.
- Dientamoeba- D.fragilis is a noncustodial forming parasite of large intestine that develops abdominal discomfort and diarrhoea.
- Cryptosporidium- A minute Cyst forming intestinal parasite that also passes to trachea or bile duct causes diarrhoea.
- Sarcocystis- A sporocyst forming protozoans that produces vomiting and diarrhoea.
- Naegleria – Cyst forming protozoans that may attack brain and cause meningoencephalitis.
Short Questions and answers on Major Groups of Protozoa:
1. Who is the biological primary host of Plasmodium?
Female anopheles mosquito.
2. Which organism causes kala-azar?
Trypanosoma gambiense.
3. What is responsible for producing Chagas' fever in children?
Trypanosoma cruzi
4. What is the cause for development of amoebic dysentery?
Entamoeba hystolytica.
5. What was the first drug used for malarial treatment and what was origin?
Quinine was the first drug used for treatment of malaria and it is collected from the bark of Cinchona.
From Major Groups of Protozoa to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.