Magnetization and Demagnetization
We will discuss here about magnetization and demagnetization.
What is magnetization?
The method of developing the properties of a magnet in a magnetic substance is known as magnetization. A magnetic substance like a piece of iron can be magnetized by electric current or by touching with a magnet. We know about the method of preparing an electromagnet and now we will discuss about the method of preparing a magnet by direct contact.
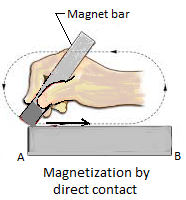
Take an ordinary bar (AB) made of iron magnetic substance).
Place it on a table and hold it firmly with left hand. Now take a strong magnet bar. Hold it with right hand in a fixed inclined position. Bring one pole of the bar magnet in contact with end A of the iron bar as shown in the figure. Now rub it down to end B of the bar along the surface. Repeat the process several times. After a few minutes the iron bar will turn into a magnet bar.
What is demagnetization?
The method of removing of the magnetic properties of a magnet is known as demagnetization. It can be done by the following methods:
1. Hitting a magnet heavily by hammer.
2. Heating a magnet at high temperature.
3. Placing two magnets with same poles facing each other.
The following uses of magnet are:
(i) Magnet is used to prepare mariner’s compass.
(ii) Electric bell and air pumps used in aquarium, are prepared with electromagnet.
(iii) Magnet is the main component of all types of speakers, telephone receivers, head phones etc.
(iv) Magnet is used to fix the door of a refrigerator.
(v) In factories heavy iron articles are lifted by very strong electromagnets
(vi) Specially designed electromagnets are used to remove iron fillings from the eyes.
From Magnetization and Demagnetization to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.