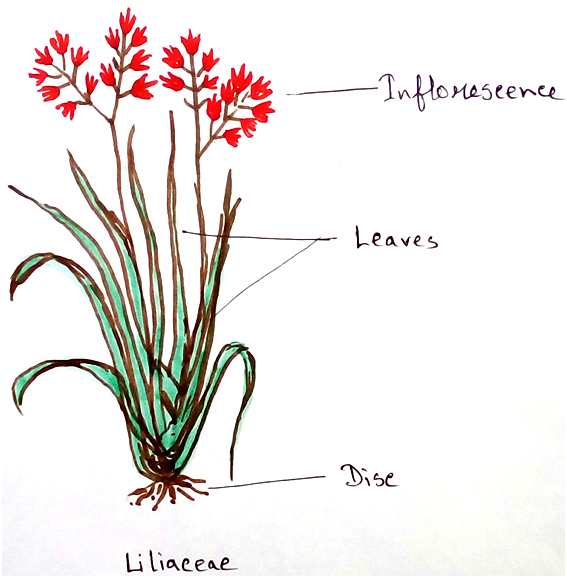
Liliaceae Family Plants
The
plants of the liliaceae family have 250 genera and 4000 species. While in India
the number is 169 species. They are considering as typical monocot family and
represent the basic monocot stock from which the other monocot family have been
arrises. It shows some similarities with some families, As it shows affinity
for Amarydilaceae, Jucaceae. But due to presence of superior ovary and axil
placentation it differs from other. Plants of this family are known as lily
family. Examples of plants are –Aloe, Lilium, Tulip etc.
Characteristics features of liliaceae are following:
1. Herbaceous plants (rarely are shrubs) having bulbs and the roots are contractile by nature.
2. Leaves are alternate or whorled along stem or in a basal resetter.
3. Simple parallel venation is observed in leaf.
4. Inflorescence are usually determinate in nature.
5. Flowers are bisexual as it contains both androecium (male reproductive part) and gynoecium (female reproductive part).
6. Flowers are usually radially symmetrical with six distinct petals, petaloid, imbricated and often with spots and lines.
7. This type of plants contains six stamens and pollen grains are monosulcate.
8. It contains six carpels which is connected with superior ovary and axil type of placentation is observed.
9. Fruits are having loculicidal capsule with usually flat and disk shaped seeds.
10. Endosperms are oily by nature.
11. Nectars are produced at the base of petals.
12. Few of them may show secondary growth . Examples are- several arborescent species of , Aloe, Yucca exhibit secondary growth of monocots.
Types of liliaceae:
The family liliaceae can be subdivided into twelve divisions. They are-
Melanthioidae – Rhizome or bulb covered with scale leaves
Herrerioideae - Have tubers, contain climbing stem with, inflorescence is small flower racemes.
Asphodeloideae – Rhizome with radical leaves and inflorescence spike.
Alliodeae – Bulb or short rhizome, inflorescence is cymose, umbel.
Lilioideae – Contains bulb ,stem contains leaf.
Scilloideae – Contains bulb, but stem leafless.
Asparagoideae – Rhizome subterranean.
Dracaenoideae – Stem are erect with leafy crown.
Ophiopogonoideae – Having short rhizome.
Aletrioideae – Short rhizome with having arrow or lanceolate radical leaves.
Luzuriagoideae – Shrubs or under shrubs with climbing twigs.
Smilacoideae – Shrubs with netvein leaves.
Economic importance of liliaceae:
I. Used as ornamental purpose - Tulips (Tulipa), Fritiallary (Fritillaria), lilies (Lilium),Trout lilies (Erythronium), etc are included in this family. This are sed for decoration, ornamental purpose.
II. Used in medicine - A.vera, A.saponaria used as components of different medicine s.
III. Used as fibre yielding plant: some plants of this group are used in yielding fibre. They are Agave sisalana (Sisal, Bahama hemp), Sansevieria roxburghiana (bow string hemp), Phormium tenax (New Zealand flax).
IV. Used as cosmetics : hyacinth is yielded from Hyacinthus orientalis. Which is a perfume. Beside this A.vera ,Aloe humulis used as cosmetics.
V. Drimia maritima (Urginea maritima)is used as a cardiac stimulator and as rat poison.
VI. Resin can be extracted from some type of plants.
Question and answer of liliaceae family plants:
1. Name a plant of liliaceae which show reticulate venation.
Answer: Similax zeylamica, S.hispida .The genus itself has been placed in a separate family named Smilaceae (Cronquist 1981, Takhtajan 1997).
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.