Leaf and Types of Leaf
Leaf is a green expanded exogenous lateral outgrowth which arises from the node of a stem or its branches. Green leaves of the plant are collectively cold foliage leaves.
Types of
leaf:
Leaves are of two types.
I: Simple Leaf – A life with undivided lamina is known as simple leaf. Depending upon the type of leaf and degree of incision, the leaves are called pinnatifid, palmatifid, pinnatipartite, palmatipartite, pinnatisect, palmatisect.
II: Compound Leaf – It is of different types. They are –
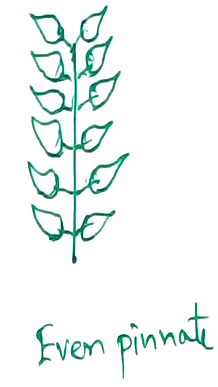
1. Pinnate compound leaf –
- Unipinnate – Cassia, rose, murraya etc.
- Bipinnate – Acacia, Mimosa.
- Tripinnate - Moringa, Drek.
- Decompound - Parthenium, Coriander, Carrot etc.
2. Palmate compound leaf – The compound leaf gives the appearance of a palm.types –
- Unifoliate – Citrus.
- Bifoliate - Balanites.
- Trifoliate – Oxalis, Aegle marmelos.
- Quadrifoliate – Paris quadrifolia, Marsilea quadrifolia.
- Multifoliate – Bombax, Cleome.
Venation – Venation is the arrangement of veins and veinletsin a lamina. They can be divided into reticulate venation and parallel or striate venation.
Reticulate Venation – Veins and veinlets of a lamina. They are of different types –
1. Pinnate or Unicostate reticulate venation- Peepal, Banyan, Mangoetc.
2. Palmate or Multifoliate reticulate venation- Zizyphus ,Luffa, Castor etc.
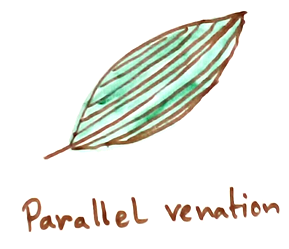
Parallel or Striate Venation – Veins run parallel without forming reticulation. Veinlets are not conspicuous. They are of different types-
1. Pinnate – Banana.
2. Palmate – Fan Palm.
Phyllotaxy – arrangement of leaf around stem or its branches are called phyllotaxy. It can be of different types. They are –
Spiral – A node bear only one leaf and successive leaves occur on opposite sides to form two alternate rows. Example - Grass.
Opposite - Two leaves occur on each node.
(i) Opposite and superposed – Opposite and successive nodes lie one above another forming only two rows (Syzygium, Quisqualis ).
(ii) Opposite and Decussate – Opposite leaf of successive nodes lie at right angles, forming four rows. Example - Guava, Calotropis.
Whorled or verticillate – more than two leaves occur at each branch. Example- Nerium.
Modifications of Leaves: Modifications of leaves can be of different types-
1. Leaf Tendrils - Leaf or leaf part are modified into tendril like structure for climbing. They are unbranched and naked. They are of different types-
- Whole Leaf Tendrils - Whole leaf is modified into tendril. Example- wild pea.
- Leaflet Tendrils - Upper leaflets are transformed into tendril. Example- sweet pea, edible pea.
- Petiolar Tendril - Petioles are elongated and sensitive to function as tendril. Example - Nepenthes.
- Rachis tendrils – Rachis and petiolules are convert to tendril. Example-Clematis.
- Rachis Tip tendril - Tip of rachis is modified to form tendril. Example- Lentil.
- Leaf tip tendril - The leaf apices are elongated and sensitive to function as tendril. Example - Glory lily.
- Stipular Tendrils – The tips of the adnate stipules produce tendrils. Examples- Smilax.
2. Leaf Spines – Leaf is converted into prickles. Example- Opuntia , Asparagus, Barberry.
3. Leaflets Hooks - Terminal leaflets are modified into curved hooks for climbing. Example- Bignonia.
4. Leaf Roots – One leaf of each node is transformed into roots for balancing on water. Example- water fern.
5. Phyllodes – Phyllodes are flattened petioles and reaches which has taken over the function of lamina. Example - Australian Acacia.
6. Leaf Bladders – Some of the leaf segments of aquatic insectivore. Example-Cyclops, Utricularia.
7. Leaf Pitchers – Lamina or whole leaf is modified into pitcher to catch insects. Example- Nepenthes.
8. Hygroscopic Appendages – Leaves are modified into hygroscopic appendages. Example - Tamarix.
From Leaf and Types of Leaf to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…












New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.