Internal Organs
We have a number of internal organs. We cannot see our internal organs. However, these organs help the body to function smoothly and keep us healthy and alive.
The internal organs are brain, lungs, heart, liver, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, bladder and kidneys.
The brain: The brain lies in the skull or head. The brain is the control centre of the body. It receives messages from all parts of the body, understands it and sends a reply message.
The lungs: The two lungs lie in the chest cavity. They are protected by the ribcage. The lungs help us to breathe.
The heart: The heart lies between the two lungs. The heart is the pumping station of the blood supply. It supplies blood to the whole body. It is the size of a fist.
The liver: The liver is the largest gland
in the body. It lies in the upper right abdomen. The liver stores food. It purifies blood. It also helps in the
digestion of food.
The stomach: The stomach lies in the upper abdomen. Food that is eaten goes into the stomach and remains there for 3 to 4 hours. The stomach helps to digest the food.
The small and large intestines: The small intestine is a very long tube which lies curled in the lower abdomen. It is surrounded by the large intestine. They also help in the digestion process.
The bladder and kidneys: These organs lie in the lower abdomen. The kidney is a bean-shaped organ. The two kidneys lie on each side of the spine in the lower part of the back. The kidneys purify the blood by removing the waste matter from it.
The bladder is a muscular organ that stores urine before expelling it from the body.
A group of internal organs work together to form a system.
Note:
When a grown-up person breathes in deeply, the lungs take in almost 6 litres of air for men and 4.5 litres of air for women. But, for normal breathing the lungs take in only half a litre of air.
Teeth and its ImportanceFrom Internal Organs to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
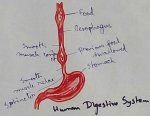
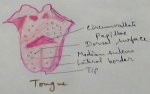
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.