Identification of a Stem
We will learn about the identification of a stem and how to differentiate a stem from root.
We have already learned that plants have two distinct parts; one grows underground and the other above ground. The underground part is the root and the other portion of a flowering plant is the shoot, which remains above ground. The shoot system of a flowering plant is composed of stem, leaves, buds, flowers and fruits.
Definition of a stem: The portion of the vascular plant, which grows towards light and holds the leaves, flowers and fruits is known as stem.
The central axis of the shoot system is called the stem. It is a rod shaped structure. At regular intervals it has slightly swollen regions, called nodes, which gives rise to leaves. Each portion in between two nodes is called internode. At the junction of a leaf and a node, a tiny outgrowth is present; it is called axillary bud. At the tip of the main stem a bud is found, which is called the apical bud.
Axillary buds grow to form branches. The branches are thinner than the main stem but they also bear similar nodes and internodes.
Some buds modify itself to grow into flowers. Flowers are the reproductive shoots of a plant. Flowers transform into fruits. These fruits bear seeds and when the seeds come on soil they germinate (initial phase in the development of a seed) and grow into baby plants.
From Identification of a Stem to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
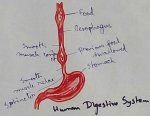
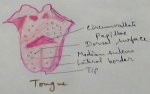
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.