Food Values
We will learn about the food values for a healthy body.
Do we know what human being needs to live?
The three basic needs of human being are food, shelter and clothing. We all need food to live and grow. Food gives us strength and energy. We should eat all kinds of food. These help us in a number of ways.
Different foods have different food values or nutrients.
Food nutrients can be divided into three groups:
(i) Some food gives us energy.
(ii) Some food protects us from diseases.
(iii) Some food helps us to grow.
Energy giving
foods:
We know some food gives us energy. Some energy giving foods are rice, chapati, potatoes, honey, sugarcane, etc. All these food items give us energy. We need energy when we work or play. Foods like butter, ghee and oil also provide us energy. They are needed by the body in small quantities. Too much of these foods, however, become difficult to digest.
Food for health:
We know some food protects us from diseases. Some of these foods are carrot, spinach, lentils, orange, milk, etc. protect us from diseases. They keep us fit and healthy. They also help us to grow. They repair the wear and tear of the body.
Food for growth:
We know some food helps us to grow. Some of these food items that help in body building are lentils, beans, peas, butter, eggs, fish, chicken, milk, etc. They are good for bones, blood and teeth. They help us to grow. They take care of the wear and tear in our body. They help regain strength.
Milk is called a complete food. It gives us energy, helps us to grow and protects us from diseases.
Hard, crisp fruits, like apples and pears, clean and strengthen the teeth and gums.
Fruits like mangoes and papaya, green leafy vegetables and carrots contain fibres which help in throwing out the solid wastes from the body.
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
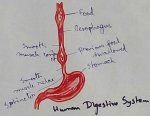
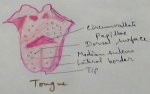
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.