Facts about Our Body
Important facts about our body to know the bones of our skeleton, the joints in different body parts, etc., Let us feel the fingers of our left hand with our right hand. We feel something hard under the soft skin. If we bend our finger we see there are three hard bones. The bones meet where there is a joint. We can bend our finger at each of these joints.
What does X-ray picture shows us?
The X-ray picture shows us the bones inside your body.
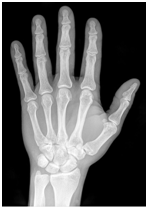
Here is an X-ray of a hand. We can count the bones in the fingers and we can also count the joints in the finger of one hand.
Lets us feel some facts about our body while studying;
(i) Feel along our neck and back we can feel the hard bones under the skin.
(ii) Feel the side and back of our head we can feel our skull.
(iii) Feel the long, thin bones on both sides of our chest these are known as the ribs.
Now let us find some other joints in our body — at our shoulder, our elbow and our wrist. Just like this, there are joints at the hip, the knee and the ankle.
At each of these joints our body can bend or turn in many ways. We will be surprised to find that our body has so many bones. All of them together make up skeleton.
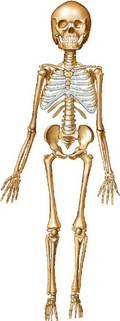
Look at the picture of the skeleton.
The bones of our skeleton give our body its shape.
What would happen if we did not have these bones?
Our body would be soft, shapeless and floppy. Our backbone helps us to stand up straight. The bones in our legs help us to stand.
Bones also protect the soft parts inside our body. Our ribs form a cage which protects our heart and lungs. Our skull is like a box which protects our brain.
The bones at the joints cannot move on their own. They need muscles to help them move.
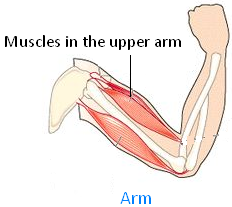
Look at the picture and we can bend our arm in the same way.
Feel the muscles in our upper arm become large when we bend our arm. There are muscles like this all over our body. Muscles help us to open and close our mouth when we speak. They help us to swallow food. They help us to smile and blink.
Some muscles of our body work all the time, even without our telling them to do so. The muscles that help us to breathe in and out never stop working. Muscles also keep our heart beating non-stop.
What else is there inside our body?
Inside our rib cage, are our heart and lungs. Watch yourself breathe. We notice the rib cage moves in and out with each breath. When we breathe in, the lungs take in oxygen from the air. When we breathe out, they push out air with more carbon dioxide.
Note:
(i) Place your hand in front of your mouth and feel the air you breathe in and out.
(ii) Run on the spot and we see that our rib cage moves faster, after running.
Our heart is made of very strong muscles. It works without stopping all through our life. It pumps blood to every part of our body.
The food we eat gets digested inside our body. It breaks up into smaller parts which the body can use. This digested food helps us to grow, gives us energy and keep us healthy. The unused part of the food is sent out of the body when we go to the toilet every morning.
The outermost covering of our body is our skin. It is soft but very strong. It bends and stretches as we move. It repairs itself when we get hurt.
Our skin helps us to feel. When we touch something, our skin tells us if it is rough or smooth, hot or cold, soft or hard.
From Facts about Our Body to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.