Factor Behind Clouds and Rain
How the sun is the main factor behind clouds and rain?
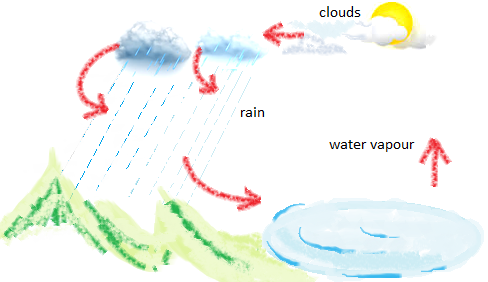
We know that due to heat from the sun shines down on the earth the water of oceans, rivers, lakes, ponds, etc gets evaporated so, the air along with the water vapour, gets warm and rises up.
As it goes higher up in the sky, it cools down.
The water vapour condenses to form tiny drops of water. Millions and millions of these droplets together form a cloud.
When the clouds pass through cooler air, they get further cooled. The water drops becomes bigger and heavier. When they become very heavy, they fall to the ground as rain. So, from here we understand that the sun is the main factor in influencing weather by giving heat to form clouds and pour rain drops.
Most of the water that falls on land goes back into the oceans, rivers, lakes, ponds, etc. Again at a certain altitude the vapours changes into clouds and clouds into rain.
This goes on repeating. This repeated change of water to water vapour, and then back to water, is called the water cycle.
From Factor Behind Clouds and Rain to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
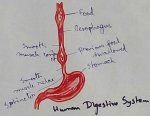
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.