Clothes we Wear
There are different types of clothes we wear and human beings are the only living things who wear clothes.
We wear clothes mainly to protect our bodies. Clothes protect us from cold, heat, dust and rain. They protect us from insects too. We also wear clothes to make us look good and smart. Early people used leaves of trees or skins of animals to cover and protect their bodies. Slowly they learnt to make clothes using cotton, wool, leather and silk. They started wearing different types of clothes.
Our clothes should be comfortable and suited to the weather conditions.
In hot places, people wear clothes made of cotton. Cotton clothes are best in summer. They are light and let the air in. They also absorb sweat. As the sweat evaporates, the body cools down. Loose fitting cotton clothes are very comfortable in hot weather. Light coloured clothes are better as they absorb less heat.
In clod places, people wear clothes made of wool, fur and leather. They prevent the body heat from escaping and keep it warm in winter.
When it rains, we wear raincoats above our clothes. Raincoats are made of material that does not absorb water and keep us dry when it rains. They prevent our clothes and bodies from getting wet.
The clothes we wear are made of cotton and cotton is made from the cotton plant. The fluffy cotton bolls growing on a cotton plant are picked and used to make cotton fibres. The fibres are woven to make cloth. We get cotton clothes from cotton plant. Animals also provide us with fibres for making cloth. The silkworm gives silk thread for making silk cloth. Sheep’s fur is woven into wool for making winter clothes. Cotton, wool and silk are used to make fur and leather clothes. They are not made of fibres.
Nylon and polyester clothes are made of fibres not obtained from plants or animals. They are called synthetic fibres.
Different people wear different clothes for their work. For example, doctors and nurses wear clothes that should be very clean, as they take care of sick people. They wear white coats of uniforms.
Soldiers wear special uniforms made of tough fibres as they live and work in very rough conditions.
Factory workers work with heavy machinery. For safety they wear overalls. As overall is one piece of cloth that cover a person from the neck to the feet. It has no portions of cloth that can get caught in the machines.
The uniforms students wear to school that belong to a particular school. The teacher and security guards of the school can easily recognise the student so that they can take care of the student.
We should take care of our clothes. If we look after our clothes well, they will last for a long time. They will also look better and make us look good and smart.
Cotton, nylon and polyester clothes can be washed with a detergent and water. They look crushed after drying, so they are ironed.
Silk and woollen clothes can be gently washed at home with a mild detergent. But it is better to have them cleaned by petrol. This is called dry cleaning.
In many places in our country, silk and woollen clothes are generally not worn in summers. They should be stored properly otherwise they can be damaged by insects. We can generally keep them in boxes along with moth balls or dried neem leaves.
From Clothes we Wear to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
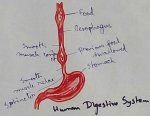
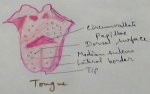
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.