Explain about Cell Membrane
Definition - Cell membrane is the thin, elastic and semipermeable living membrane that surrounds the protoplasm of a cell is called cell membrane o plasma membrane or plasma lemma.
Existence of cell membrane was first observed by Nageli and Cramer in 1856.Then in 1931 it was named as plasma lemma by Plowe.It is find in each and every living cells including both plants and animals. It is formed due to modification of peripheral layer of cytoplasm.
Structure of the cell membrane- Cell membrane in some cases (renal tubules, intestinal mucosa ) form finger like projections called microvilli, phagocytic vacuoles, cilia, flagella, branched tubular structure called lamella are observed.
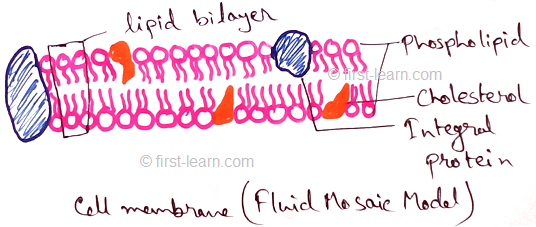
Ultrastructure of the cell membrane - it is found due to the study of cell membrane under electron microscope. In 1935 Danielli and Davson define the cell membrane as trilamellar structure which is made up of lipoprotein (lipid and protein). Average thickness of the cell membrane is 7.5 nm where each of two protein layers are about 20 angstrom and the middle layer is 35 angstrom thick. The lipid layer is made up of phospholipid molecules. This layer is called bimolecular phospholipid layer.This layer has two end one is hydrophobic and another is hydrophilic.
1972 Singer and Nicolson described fluid mosaic model of cell membrane. According to fluid mosaic model of cell membrane –phospholipid bilayer contains discontinuous mosaic of globular proteins . The matrix is in fluid form so the randomly distributed proteins are relatively free to move.Different organisms have different ratio of protein – lipid ratio. Structurally membrane contains two types of protein. One of them is intrinsic and another is extrinsic protein. Extrinsic proteins are called peripheral protein which is associated with the membrane surface. They are dissociable and situated outside the membrane. Intrinsic proteins are called integral proteins which are partially penetrating throughout the thickness.
According to function membrane proteins can be divided into three groups- structural protein (backbone of the membrane), carrier proteins (transport molecules), enzyme or receptors protein (catalytic function).
Functions of cell membrane are –
1. It provides proper shape of the cells of animal .
2. It also acts as only covering of cell boundaries.
3. Cell membrane can separates protoplasm from the extra cellular fluid so that it can maintain the individual identity of the cells and protects the cytoplasmic organelles.
4. In an animal tissue ,the cell membrane forms linkages or places of close contact between the adjacent cells which may help in structural and functional integrity.
5. Cell membrane also have the capacity to respond to the stimulus of the living cells.
6. Some of the biomolecules much as chemical , molecular receptors are sensitive to sensitive to the hormones, neurotransmitters and regulate the function of target cell.
7. It also acts as medium of transport (semipermeable) membrane and enhance the materials from protoplasm and extra cellular fluid.
8. Membrane transport are of two types , passive transport (it is governed by concentration gradient), active transport ( energy dependent process of transport against concentration gradient).
From Cell Membrane to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like… -
Explain Transport of Gases | External Respiration | Tissue Respiration
Oct 09, 25 11:35 PM
In humans gaseous exchange is completed in the following ways the steps are - External Respiration or Breathing - Breathing in false taking in of Oxygen and giving out of carbon dioxide in the body. M…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.