Birds and its Food Habits
We will learn about different birds and its food habits.
Birds are the only animals which have feather on their bodies. Like us, birds have two feet. They do not have arms like us, but have wings in place of arms. These wings are attached firmly to their bodies. They have strong muscles to flap them. Wings are very useful to birds. Most of them can fly with the help of their wings.
Most birds are very light in weight due to their thin and hollow bones. Observe the body shape of a bird, it looks like an airplane. The front part of its body is thin but the middle part is broad. This helps them to fly. Birds use their tails to turn or change the direction during flight.
First, a bird jumps in the air and flaps its wings. This helps to push it upwards and forwards in the air. For landing, it spreads its wings and comes down.
Some birds like eagles and vultures fly very high while some birds like parrots, sparrows and crows fly at a low height. Some birds like the kiwi and ostrich are unable to fly although they can run very fast. We will be surprised to know that there are nearly 8600 known kinds of birds in the world.
Birds
and its food habits:
Different birds have different food habits. Birds like parrots and pigeons eat seeds and fruits. Birds like crows and ducks eat both, plant produce and flesh of other animals. Birds like eagles and vultures eat the flesh of other animals.
Animals and its Feeding Habits
Movement and Shelter of Animals
Nesting HabitsFrom Birds and its Food Habits to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
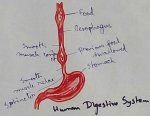
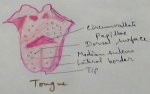
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b… -
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
Jun 15, 25 03:20 PM
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from an…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.