All Vertebrates are Chordates but All Chordates are Not Vertebrates
Chordates: Chordates are the animals belonging to the phylum chordata. It contains notocord, nerve cord, pharangeal slits, endostyle, post anal tails for atleast their some phases of life cycle.Chordata are divided into four groups – hemianatropous Chordata, eurochodata, cephalochordata, vertebrata.
Characteristics features of chordates:
1. Presence of notochord - In vertebrates notochord act as the primary axis of the body and it provides skeletal support to the body throughout the life.
2. Presence of nerve chord - The hollow nerve chord- derived from the ectoderm which is then enrolled into solid tube. During embryonic development nerve chord is converted into brain and spinal cord in vertebrates.
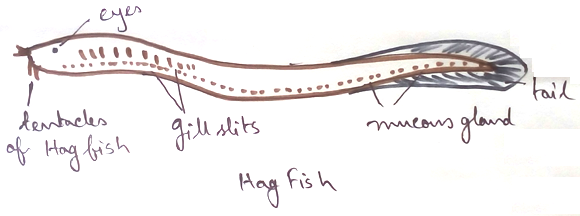
3. Presence of pharyngeal slits - Pharyngeal slits are the portion which is just behind the opening of mouth and is released upto the environment. In vertebrates some organisms like fish contains pharangeal slits and formed gills which help the fish to intake oxygen from water and release the excretory products. But in case of higher vertebrates like mammals, birds they don’t have pharangeal slits during mature stage. They only contains pharangeal slits during embryonic development and during birth pharangeal slits are converted into jaws and bones of inner ear.
4. Post anal tail – It is the posterior elongation of the body which is extended beyond the anus. The tail contains bones and muscles in fishes which help them in locomotion and change direction in the water. But in case of terrestrial animalstails are used balanced, courting and signalling when they are in danger. In some species like ape, human, tails are present during embryonic development but in adult it converts into vestigial organs.
5. Endostyle - It is an organism which developed in lower vertebrates (urochordata, cephalochordata, larva of lamprey) for filter feeding. It also secrets mucous that help in trapping food and coat the cilia.
6. Cephalisation – Well developed and brain has been evolved in the region of head.
7. Organisation - Chordates are triploblastic and true coelom is present.
Vertebrates: It is the largest subphylum of the chordates which is characterized by the formation of cranium and vertebral column instead of notochord and brain spinal chord instead of notochord and brain, spinal cord instead of dorsal nerve cord.
Characteristics features of vertebrates:
1. Dorsal nerve chord differentiated into brain and spinal cord.
2. Exoskeleton and endoskeleton is differentiable.
3. Notochord- is replaced by vertebral column around the spinal cord and cranium around the brain.
4. Heart is ventral and blood contains haemoglobin.
5. Gill slits occur in atleast embryo stage.
6. Excretory organ is kidney.
7. Paired lateral appendages, tail, endocrine glands, autonomous nervous system and portal system (hepatic,renal, hypophyseal) are the other traits present in the subphylum vertebrates.
8. According to the presence and absence of jaw it can be divided into gnathostomata (with jaw), agnatha (without jaw).
In vertebrates notochord and nerve cord are present only in embryonic stage but it is replaced by cartilaginous and bony vertebral column and brain and spinal chord in their adult stage. In case of other lower vertebrates (hemichordata, urochordata) notocord is present. Thus all vertebrates are chordates but all Chordates are not vertebrates.
From All Vertebrates are Chordates but All Chordates are Not Vertebrates to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.