Addition of Whole Numbers
Whole numbers are positive integers including zero. The main difference between whole numbers and natural numbers is that natural numbers are also positive integers but does not include zero. Hence we can say that natural numbers means whole numbers whereas, whole numbers does not mean natural numbers.
Example : { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, ………..}
There are main four types of operation done in whole numbers that is addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Any negative integer, fraction or decimal is not considered as whole numbers. Whole numbers are often called as counting numbers however, counting numbers does not include zero as zero cannot be counted. So counting numbers along with zero is termed as whole numbers.
The first or the most basic operation of whole numbers is ADDITION.
The steps for addition of whole numbers are as follows:
I. Firstly the numbers are written under ones, tens, hundreds, thousands, ten thousands and so on
II. Then starting from the ones column they are added. If there is any carry over in the ones column then that is adjusted in the tens column. Furthermore, if there is any carry over in the tens column then that is adjusted in the hundreds column and so on.
Examples of addition of 2 digit whole number without carry over:
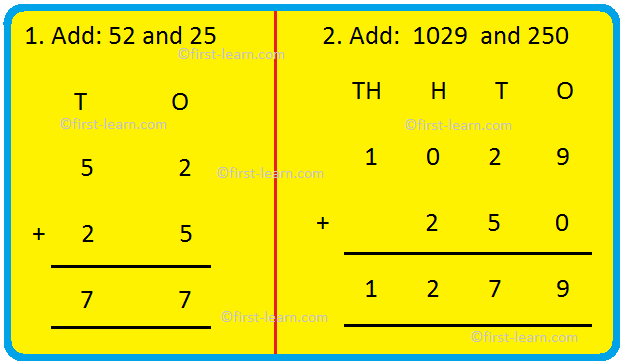
1. Add: 52 and 25
T O
5 2
+ 2 5
7 7
Here in the ones column 2 + 5 = 7 and in tens column 5 + 2 =7. That gives the answer 77
2. Add: 73 and 16
T O
7 3
+ 1 6
8 9
Here in the ones column 3 + 6 = 9 and in tens column 7 + 1 =8. That gives the answer 89
Examples of addition of 3 digit whole number with carry over:
3. Add: 103 and 89
H T O
1 0 3
+ 8 9
1 9 2
Here in the ones column 3 + 9 = 12. But we cannot write 12 hence 2 is written in the ones column and 1 is carried over in the tens column. Therefore the subtotal of tens column will be 0 + 8 + 1 (carryover) = 9. In hundreds column only 1.
Examples of addition of 4 digit whole number without carry over:
5. Add: 1029 and 250
TH H T O
1 0 2 9
+ 2 5 0
1 2 7 9
Here in the ones column 9 + 0= 9. In the tens column 2 + 5= 7 and In hundreds place 0 + 2 = 2 , in thousands place only 1.
Examples of addition of 4 digit whole number with carry over:
7. Add: 3569 and 2510
TH H T O
3 5 6 9
+ 2 5 1 0
6 0 7 9
Here in ones place 9 + 0 is 9 and in tens place 6 + 1 =7 with no carry over in these two places. However, in the hundreds place 5 + 5= 10 there will be a carryover. We cannot write 10 so we will write only 0 and 1 would be carried over in thousands place. Therefore the subtotal of thousands place will be 3 + 2 + 1 (carryover) = 6
8. Add: 4315 and 1659
TH H T O
4 3 1 5
+ 1 6 5 9
5 9 7 4
Here in the ones place 5 + 9 = 14 so 1 will be carryover in tens place and we will write only 4 in ones place. The subtotal of tens place will be 1 + 5 + 1 (carryover) = 7 with no carryover. In the hundreds place 3 + 6 =9 with no carryover and again in the thousands place 4 + 1 = 5 with no carryover as well.
From Addition of Whole Numbers to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
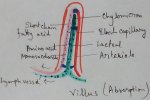
Absorption of Digested Products | Absorption of Water | Nephrons
Jul 09, 25 02:24 PM
Food and water is observed in different parts of the body and is distributed in different cells and tissues. Absorption of food is observed to be observed in the small intestine in the specific type o… -
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Math
Jun 27, 25 12:26 AM
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way. -
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Jun 27, 25 12:20 AM
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth. -
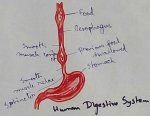
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Jun 21, 25 01:15 PM
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which sta… -
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Jun 18, 25 01:34 PM
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite b…

New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.