Wind, Storm and Breeze
In moving air we will learn about wind, storm and breeze.
We can feel the air when you run, cycle or swing. This is because the air is moving against your face.
Nancy liked to play with balloons. She filled one with water. It got bigger as the water in it needed space.
Nancy took another balloon. She blew into it and filled the balloon with air. She kept the balloon near her face and opened it. She could not see the air but she can fell it. Yet it took up space inside the balloon. That is why it became bigger.
|
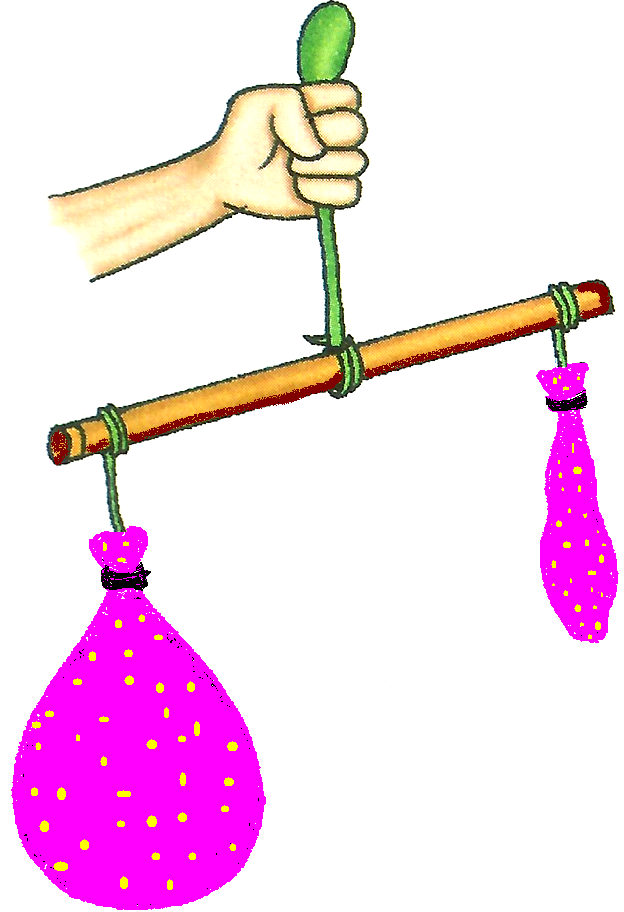
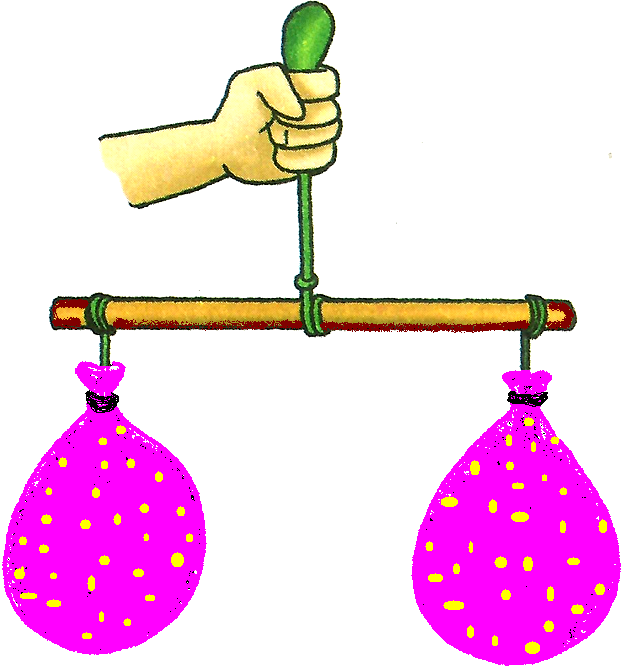
Then she blew up two balloons using a cycle pump. She tied the two balloons to the two ends of a stick. Using a pin, she pricked one of the balloons. The air leaked out from the balloon. The balloon became smaller. It looked just like a thin skin. The stick came down on one side. One balloon still had air inside it. That is why it was heavier. Although we cannot see the air but it has weight. |
Air is all around us. We cannot see or touch it, but we can feel it when it moves. For example, make a paper fan and wave it near your face. We can feel the air.
What is wind?
Moving air is called wind. We come to know there is a wind, when a wind makes things move. It makes a kite fly. It moves clouds in the sky.
Moving air (wind) can make the things like kite, sail boat and windmill work.
What is breeze?
A gentle wind or when the wind blows slowly, it is called a breeze.
We can find out the direction of the wind. We can do an experiment; take some sand in your hand. On releasing the sand, it falls in the direction of the wind.
What is storm?
Fast and strong winds cause a storm. A storm can blow away things. Storms can damage buildings. They can uproot trees and spoil crops. They can also cause damage to plants, animals and human beings.
What is gale?
A very strong wind is called a gale. Strong gales can uproot the plants and cause a lot of damage.
A windvane tells us the direction of the wind. The beak of the cock in the windvane points the way in which the wind blows.
We know, winds can be useful too. On a hot day, a breeze keeps us cool. That is why we use coolers and fans in summer. A wind helps washed clothes dry quickly. Winds can carry light seeds to new places. There, they become new plants. Winds turn the fans on windmills. These can make electricity.
From Wind, Storm and Breeze to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Amphibolic Pathway | Definition | Examples | Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Jun 06, 24 10:40 AM
Definition of amphibolic pathway- Amphibolic pathway is a biochemical pathway where anabolism and catabolism are both combined together. Examples of amphibolic pathway- there are different biochemical… -
Respiratory Balance Sheet | TCA Cycle | ATP Consumption Process
Feb 18, 24 01:56 PM
The major component that produced during the photosynthesis is Glucose which is further metabolised by the different metabolic pathways like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, TCA cycle and produces energy whic… -
Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation | ETC |Diagram
Feb 04, 24 01:57 PM
It is also called ETC. Electron transfer means the process where one electron relocates from one atom to the other atom. Definition of electron transport chain - The biological process where a chains… -
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle | Krebs Cycle | Steps | End Products |Diagram
Jan 28, 24 12:39 PM
This is a type of process which execute in a cyclical form and final common pathway for oxidation of Carbohydrates fat protein through which acetyl coenzyme a or acetyl CoA is completely oxidised to c… -
Aerobic Respiration | Definition of Aerobic Respiration | Glycolysis
Dec 15, 23 08:42 AM
This is a type of respiration where molecular free oxygen is used as the final acceptor and it is observed in cell. Site of Aerobic Respiration - Aerobic respiration is observed in most of the eukaryo…




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.